Solar Radiation Sensors: Types, Applications, and Benefits
Introduction to Solar Radiation Sensors:
Solar radiation sensor are key instruments for measuring solar energy, available in several types with numerous applications. This article discusses their classification, explores various application scenarios, and underscores the advantages they offer.
1. Types of Solar Radiation Sensors:
Solar radiation sensors are categorized based on their measurement methods and functionalities:
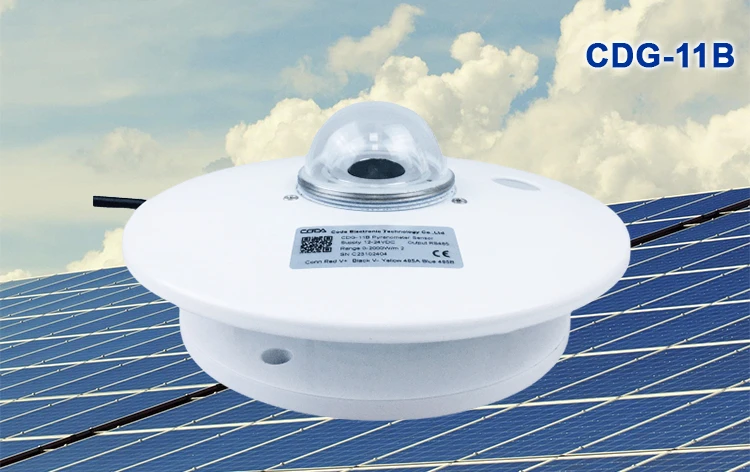
a) Pyranometers:
These sensors gauge total solar radiation—both direct and diffused—received on a horizontal surface. Meteorological stations, solar power setups, and farming research frequently include them.
b)Pyrheliometers:
Measure direct solar radiation, also known as direct normal irradiance (DNI). Researchers use them for solar resource assessment, system design, and atmospheric research.
c)Pyrgeometers:
Measure the longwave infrared radiation from the Earth’s surface and atmosphere. They are important for studying the Earth’s energy balance, climate change, and weather prediction.
d) UV Sensors:
These sensors measure ultraviolet radiation from the Sun. They help monitor UV exposure for health, environmental conditions, and sterilization processes.
e) Spectroradiometers:
These instruments measure solar radiation across the entire electromagnetic spectrum. They provide detailed spectral data for solar energy research, atmospheric analysis, and material characterization.
2. Common Applications of Solar Radiation Sensors:
Solar radiation sensor are employed across diverse fields and industries in scenarios such as:
a) Solar Energy Systems:
They improve how photovoltaic panels, solar thermal systems, and concentrated solar power plants work. They do this by providing accurate solar irradiance measurements.
b) Weather Monitoring:
These sensors are used in weather stations. They provide important data for forecasting, climate research, and studying the Earth’s energy balance.
c) Agricultural Research:
These sensors measure sunlight. They help assess crop growth, improve irrigation methods, and study how sunlight affects plant health and yield.
d) Environmental Monitoring:
Employed in environmental studies to analyze solar radiation’s effects on ecosystems, track UV exposure, and assess climate change’s impact on habitats.
e) Building Energy Efficiency:
These sensors help manage energy in buildings. They optimize natural light and control shades. This reduces energy use and improves efficiency.
3. Benefits Offered:
Solar radiation sensor deliver considerable benefits across various applications:
a) System Performance Optimization:
Accurate irradiance measurements from these sensors lead to enhanced solar energy system performance, yielding higher energy output and cost efficiency.
b) Resource Assessment:
They evaluate solar energy potential at specific sites. This helps in choosing the best locations for installations. It also predicts energy generation and guides investment decisions.
c) Research and Development:
They are integral to scientific inquiries into solar energy, weather monitoring, climate studies, and environmental assessment.
d) Energy Efficiency:
By tracking solar radiation levels, these sensor aid energy optimization in buildings, reduce dependency on artificial lighting, and boost overall efficiency.
e) Sustainability and Renewable Energy Transition:
Solar radiation sensors support renewable energy development like solar power, fostering a shift towards more sustainable practices.
Conclusion:
Researchers utilize different types of solar radiation sensors in areas like solar energy systems, weather tracking, farming, and environmental studies. Their value lies in optimizing performance, aiding resource evaluation, supporting research endeavors, enhancing energy efficiency, and promoting sustainability. By accurately measuring solar irradiance, these sensors are pivotal in utilizing solar power effectively and advancing the transition to clean renewable energy sources.