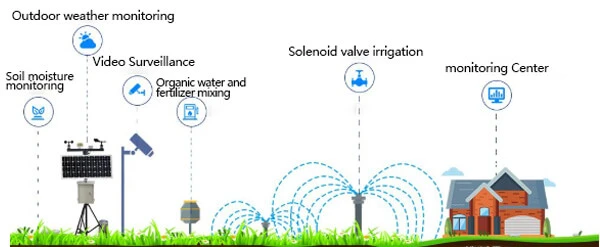
irrigation sensors system | accord irrigation technologies
Soil moisture and rain sensors are important for irrigation systems in farming. They help monitor key environmental data. This data is vital for growing crops. It includes soil moisture, temperature, nutrient levels, air humidity, and light intensity.
Using data from these sensors, irrigation controller systems can plants watered accurately. This means water is given exactly when and where it is needed. This method helps save water, cuts down waste, improves growing conditions, and supports sustainable farming.
In a smart irrigation system, sensors send data wirelessly to the cloud or a smart controller. Researchers use this data to make irrigation plans based on algorithms and the needs of the crops..
These guidelines can control irrigation tools like solenoid valves and pumps. This allows for remote control and smart monitoring. Users can see data in real-time.
They can also make changes using mobile apps. This makes managing irrigation more flexible and efficient.
Irrigation systems often use different types of sensors to check and manage their operations. Here are some key examples:
1.Soil moisture sensors:
It is important to measure how much water is in the soil. Soil moisture sensors are key for any irrigation system. Their main job is to help farmers decide if irrigation is needed. They also help find the best amount and timing for watering.
Soil moisture sensors are placed in the fields. They give information about moisture levels. Farmers use this data to decide how much to water.
This depends on the needs of the crops and the soil. When linked to smart irrigation systems, these sensors help manage watering automatically.
When soil moisture gets too low, the system turns on pumps and sprinkler systems to water the soil. When there is enough moisture, it turns off the water supply. This method helps use water better and reduces waste. It also ensures crops get the water they need.
2. Soil Temperature Sensors:
These sensors measure soil temperature. This information can help with irrigation decisions, especially during extreme weather.
People often put temperature sensors right in the soil. These sensors provide accurate readings. When you mix these readings with moisture data, you see a clear picture of soil conditions. This helps in planning the best weather based irrigation.
3. Flow Sensors:
This tool measures the flow of water or fertilizer. It helps make sure they are spread evenly.
Technicians place flow sensors at key spots like pump outlets or inside pipelines. They help track water use and find problems like leaks or blockages.
4. Pressure Sensors:
The job is to check water pressure in the system. This makes sure the right areas get enough flow.
5. Level Sensors:
Check water levels to avoid system overloads or shortages.
These sensors use technologies like pressure detection, ultrasound, or floats. They measure water levels in sources or reservoirs. This helps farmers manage water resources better.
6. pH Sensors:
These devices are important for water with chemicals. They measure how acidic or basic the water is.
7. Rainfall Sensors:
Monitor rainfall to avoid too much water or flooding.
Rain sensors measure how much it rains. This helps farmers adjust their watering schedules based on the weather. When the sensors detect enough rain, they can stop watering automatically. This prevents wasting water.
8.Wind irrigation systems:
Use wind speed sensors to check wind conditions. This helps you use wind more effectively.
9.Humidity and Temperature:
Sensors are important for measuring humidity and temperature. This information helps us know how much to water plants.
10.Evapotranspiration meters:
Measure how fast water evaporates from the soil surface. Usually, this involves a container filled with water that tracks changes in water level over time.
Farmers can learn how quickly water evaporates. This helps them see how much water the soil loses. They can then change their irrigation horticulture conservation and technology schedules. This way, they can cut down on evaporation and save water.
These sensors help improve irrigation management. They make water use more efficient and support healthy plant growth.
The Role and Value of Sensors in Agricultural Irrigation
Integrating these rain and moisture sensor for irrigation system is vital for agriculture, offering several benefits:
1. Water Conservation:
Sensors give data on soil moisture, rainfall, and evaporation rates. This helps farmers understand soil and environmental conditions. With this information, they can figure out the right amount of irrigation water needed.
This helps stop over-watering and cuts down on water waste. These methods make water use better and reduce stress on groundwater and rivers. They also support farming that is good for the environment.
2. Better Crop Yield and Quality:
Sensors help farmers monitor soil moisture and temperature. This allows them to time and adjust irrigation for their crops.
Providing the right water and temperature helps plants grow better. It supports root development, nutrient absorption, and photosynthesis. This, in turn, boosts crop yield and quality.
3. Lower Pest and Disease Risks:
Real-time data on soil moisture and temperature helps farmers monitor plant growth. By adjusting irrigation frequency and amounts, they can reduce the risk of pests and diseases. Too much moisture can lead to root rot and promote disease, while dry conditions may attract pests like mites. With sensor data, farmers can quickly change irrigation strategies to protect their crops.
4. Enhanced Agricultural Management Efficiency:
Combining sensor data with automation and remote monitoring helps manage irrigation systems better. Farmers can control irrigation using apps or computers. They can access data anytime and manage operations from afar. This method saves time, cuts labor costs, and makes systems more efficient and reliable.
In summary, soil moisture and rain sensors for irrigation systems are very important for farming. They help farmers use water more wisely.
This helps crops grow better and be of higher quality. It also lowers the risk of pests and diseases. Plus, it makes farming more efficient and sustainable.