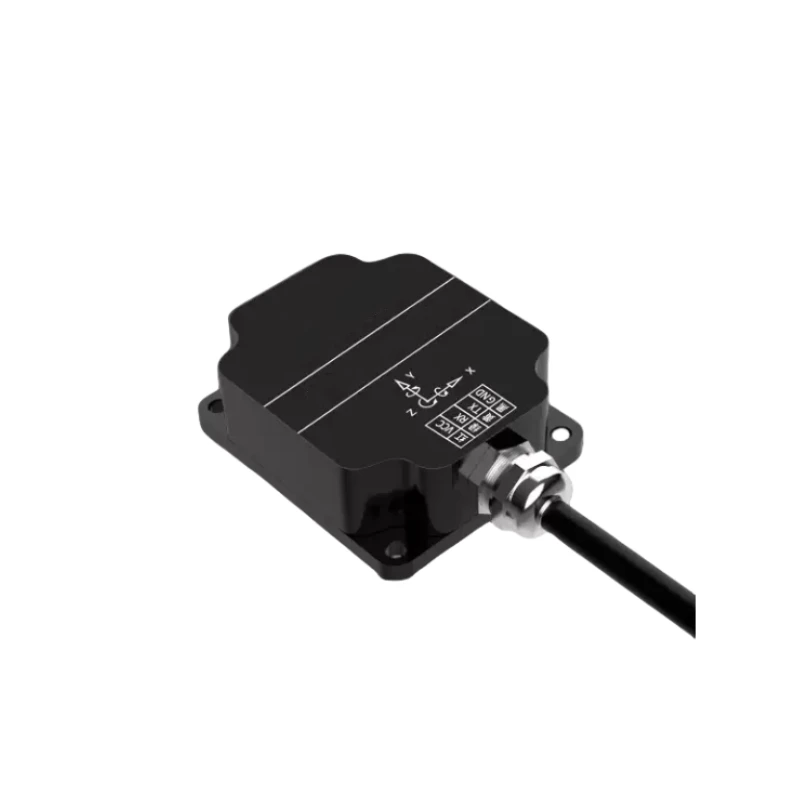
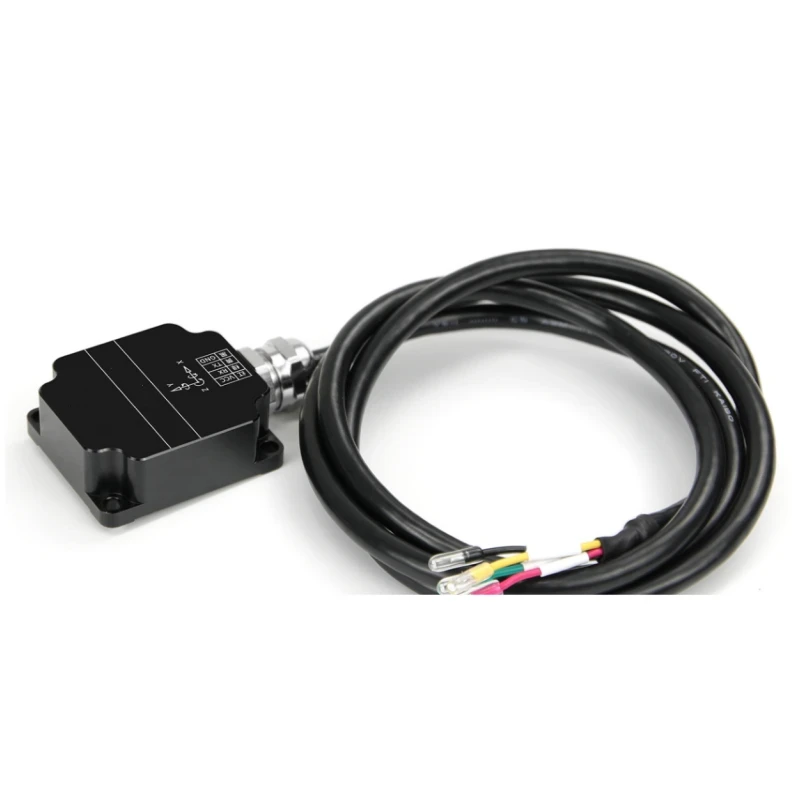
Description
CDS-10A Tilt Displacement Sensor
Engineers design a tilt displacement sensor, also called a tilt sensor or inclinometer, as an electromechanical or electronic device. It measures the angle of inclination, tilt, or displacement relative to gravity. We design this sensor to detect changes in orientation. It translates the physical movement or tilt into an electrical signal, and we can then analyze and process this signal.
Many modern tilt displacement sensors utilize MEMS technology. In a MEMS – based tilt sensor, a small, suspended mass is placed on a flexible structure. When the sensor tilts, the mass moves due to the influence of gravity. This movement is detected by capacitive, piezoresistive, or piezoelectric elements. For example, in a capacitive MEMS tilt sensor, the movement of the mass changes the distance between two electrodes, altering the capacitance. The change in capacitance is then converted into an electrical signal proportional to the tilt angle.
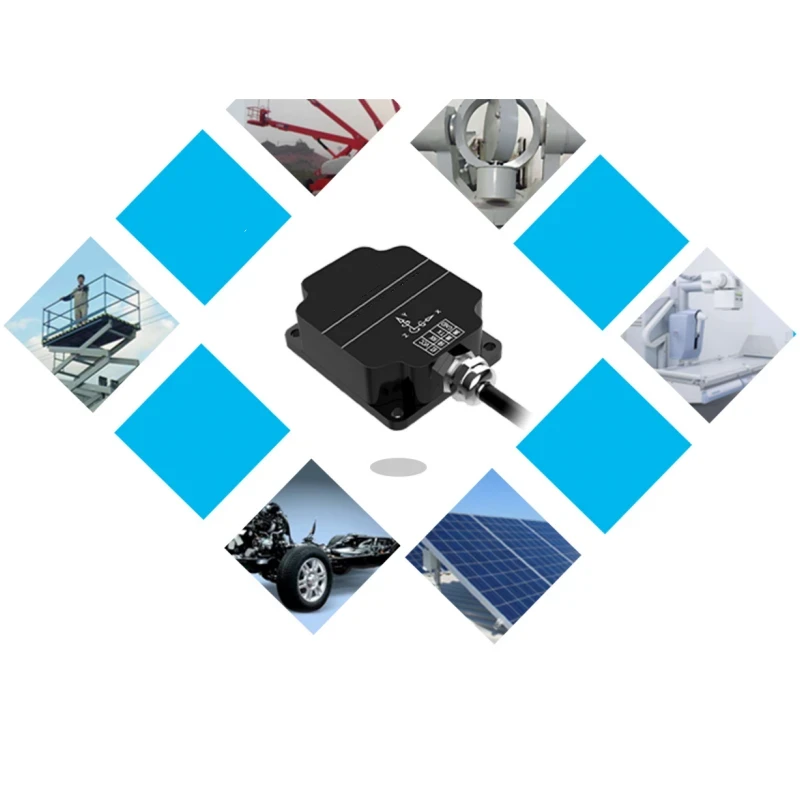
Application
◉Tilt displacement sensors are used in vehicle stability control systems. They help detect the vehicle’s tilt during cornering, acceleration, and braking. This information is then used by the vehicle’s control unit to adjust the braking and throttle systems, preventing skidding and rollovers.
◉Tilt sensors play a crucial role in robotics, especially in mobile robots. They help robots maintain balance, navigate uneven terrains, and perform tasks that require precise orientation control. For example, a cleaning robot can use tilt sensors to detect and avoid stairs or inclined surfaces.
◉In aircraft and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), tilt sensors are used to measure the pitch, roll, and yaw angles. This information is essential for flight control systems to maintain stable flight and ensure the safety of the aircraft.
Sensor News
The Working Principle And Applications Of Gas Sensors












