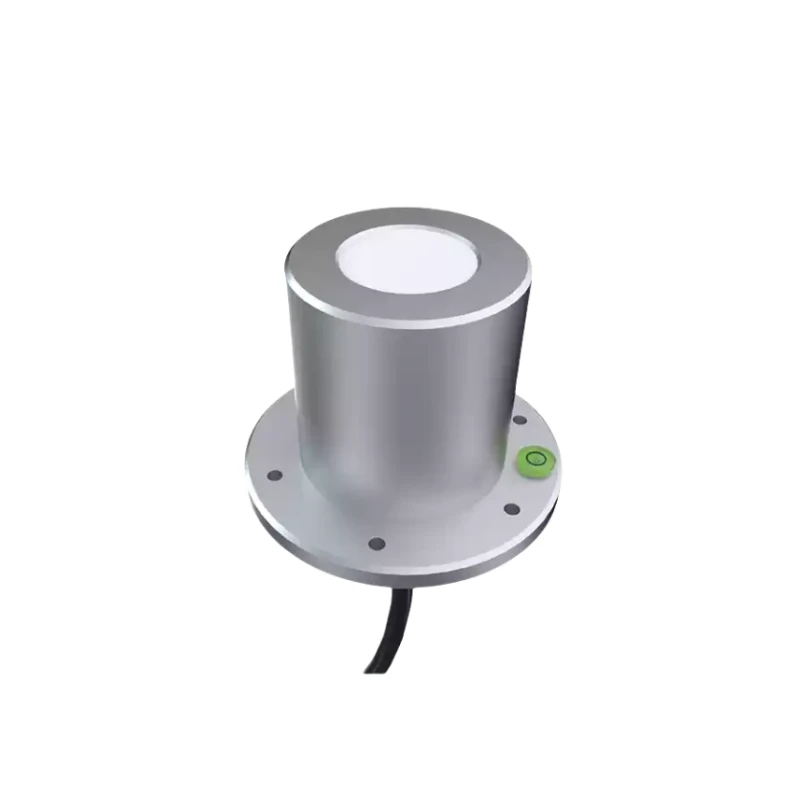
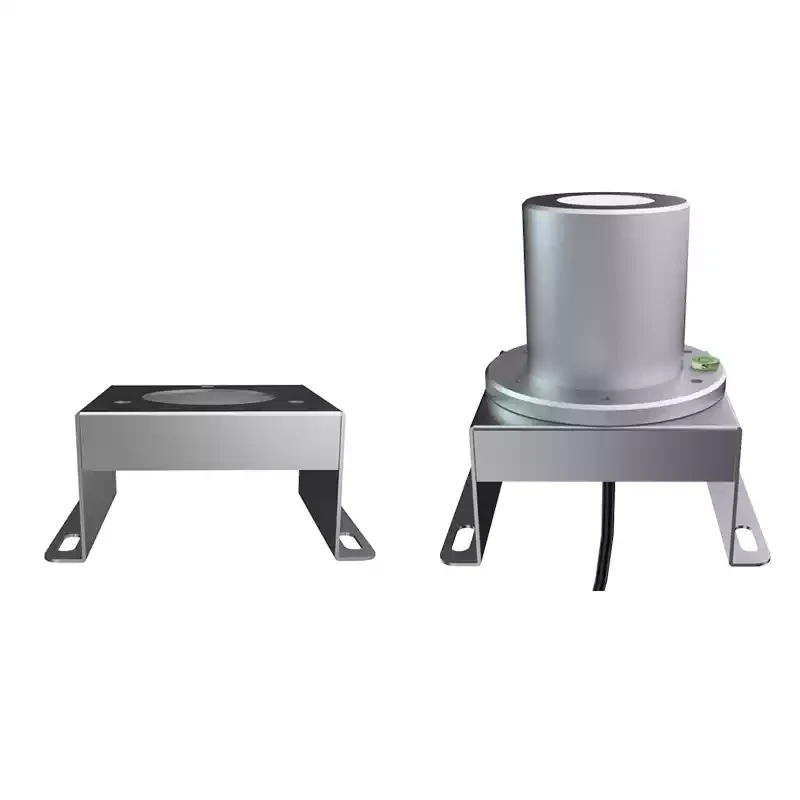
Description
CDG-15B Sunshine Hour Sensors
CDG-15B Sunshine hour sensors are important tools for weather and environmental monitoring. These sensors track how long direct sunlight shines on a certain area. They use different technologies, such as optical sensing, to find changes in light intensity and wavelength.
This helps them see when the sun shines bright enough to count as sunshine hours. Some sensors use smart algorithms to tell apart direct sunlight and diffused light. This helps ensure accurate readings.
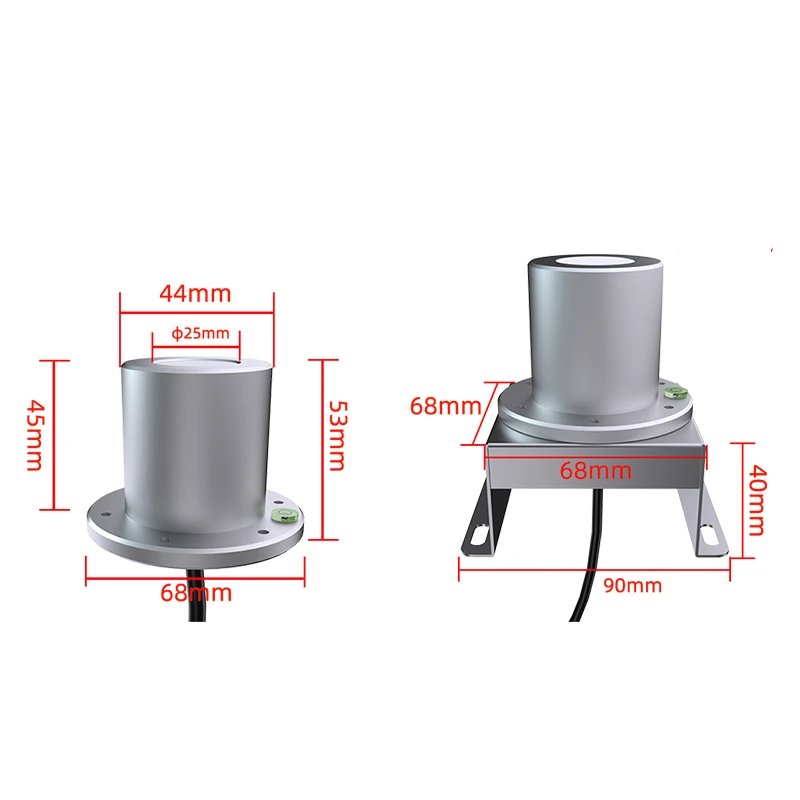
Installation & size
Application
◉Crop Growth Optimization
In farming, sunshine hour sensors are very important. Different crops need different amounts of sunlight. This sunlight is important for photosynthesis, growth, and development. For example, crops that love the sun, like tomatoes and peppers, need many hours of sunlight to grow lots of fruit.
By measuring sunshine duration, farmers can predict how fast their crops will grow. This helps them decide when to plant, water, or fertilize. If the sensor shows that sunshine hours are lower than what a crop needs, farmers may change their methods. They might use artificial lights in greenhouses to add more sunlight.
◉Solar Power Potential Assessment
For the solar energy industry, sunshine hour sensors are important tools. They help in choosing sites and designing systems. When planning to install a solar power plant, developers must know the solar energy available at the site.
This information is crucial for their project. Solar energy experts can estimate how much electricity solar panels will make. They do this by measuring sunshine hours.
They view places with lots of sunshine, like deserts, as good locations for big solar power projects. Also, data from sunshine hour sensors helps to size the solar power system properly.
This data helps us find out how many solar panels we need. It also helps find out what type of panels are needed. It predicts energy output and return on investment over time.
◉Climate Pattern Analysis
Climate scientists rely on sunshine hour sensors to study long – term climate patterns. Changes in the number of sunshine hours over time can provide insights into climate change.
For example, fewer hours of sunshine in a region could mean more cloud cover. This might be linked to rising temperatures, changes in air patterns, or pollution.
Scientists can make better climate models by using historical data from sunshine hour sensors. They also look at other climate factors, such as temperature, rainfall, and wind patterns. These models help predict future climate scenarios. They also help us understand the complex interactions in the Earth’s climate system.
Sensor News
What Different A Solarimeter From A Pyranometer?