Overview of Weather Measuring Devices
Weather measuring devices, also known as meteorological equipment, include various tools. These tools are made to check and record various weather conditions. These tools are very important in many areas. They are used in weather stations, to check the environment, in farming, in flying, and for navigation.
They provide accurate and reliable weather data. Here is a simple explanation of important weather tools and what they do:
I. Devices for Measuring Temperature
1.Platinum Resistance Temperature Sensor
– Function: Detects the temperature of air, soil, and different items.
– The working principle is simple. The resistance of platinum changes when the temperature changes. You can find the object’s temperature by measuring its resistance value. Common Pt100 sensors are made from ceramic, glass, and mica.
2. Digital Thermometer
– Purpose: It records and shows the air temperature.
– Features:
– Digital Display: Provides precise temperature readings in Celsius or Fahrenheit.
– Maximum and Minimum Temperature Record: This keeps track of the highest and lowest temperatures for a certain time.
II. Humidity Measuring Devices
1. Moisture-Sensitive Capacitive Humidity Sensor
– Purpose: Measures atmospheric relative humidity.
– Working Principle: It is made of a small capacitor that uses an organic polymer as the dielectric. As the polymer membrane takes in or gives off water vapor, its dielectric constant changes with the humidity. This change affects the capacitance. This capacitance is turned into a voltage change to find the relative humidity level.
2. Humidity Meter (Hygrometer)
– Purpose: It checks and measures the levels of air humidity.
– Features:
– Digital Display: Clearly shows the relative humidity as a percentage.
– Dew Point Indication: Shows the temperature when moisture in the air starts to condense.
III. Wind Measuring Devices
1. Wind Cup Anemometer
– Purpose: Measures wind speed.
– Working Principle: It has three rotating cups that turn a multi-tooth disc. The rotation creates a pulse signal based on the speed of the wind cup. This signal is then changed into a real wind speed value using a counter.
2. Wind Direction Sensor
– Purpose: Determines the direction of wind flow.
– Working Principle: It shows wind direction with a directional arrow. This arrow is linked to a coaxial code disc. The disc shows a value that matches the direction of the wind.
There are different types of sensors. These sensors include photoelectric, voltage-based, and compass-based types.
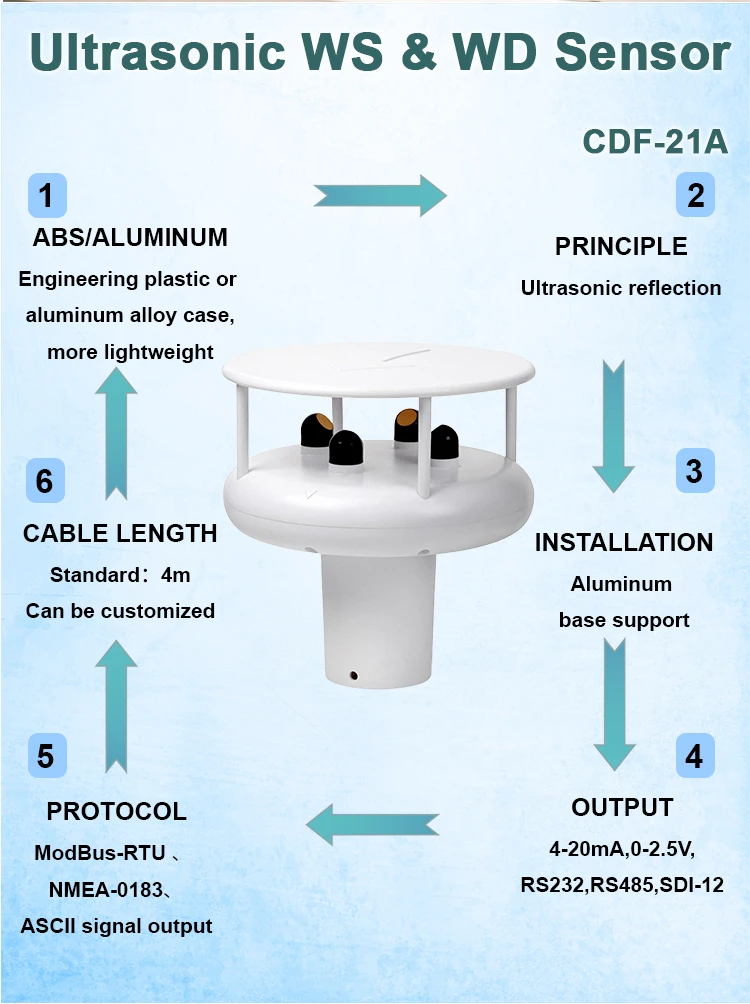
3. Ultrasonic Wind Speed and Direction Sensor**
– **Function:** It simultaneously gauges both wind speed and direction.
– **Operation:** Uses the time it takes for sound waves to travel in the air. This helps us quickly find the speed and direction of the wind. It also prevents wear and tear.
IV. Devices for Measuring Atmospheric Pressure
1. **Capacitive Pressure Sensor with Silicon Membrane Box**
– **Purpose:** Measures atmospheric pressure.
– **Operation:** Uses a vacuum-sealed box made from thin film of monocrystalline silicon. When the upper and lower diaphragms change shape due to pressure, we can notice changes in capacitance. These changes match variations in atmospheric pressure.
2. **Smart Fully Compensated Digital Barometric Pressure Sensor**
– **Function:** Accurately gauges atmospheric pressure with great precision.
– **Operation:** The sensing part is a silicon capacitor. It is housed inside the collector chassis. It connects to outside air through a pressure tube. This allows for quick and accurate pressure detection.
V. Precipitation Measuring Devices
1. **Tipping Bucket Rain Gauge**
– **Purpose:** Records rainfall measurements.
– **Operation:** The device has two triangular water buckets. They rotate around a central axis. Each time it rotates, a magnet turns on.
This turns on a reed switch and makes an electrical pulse. The number of rotations shows how much it rained.
2. **Rain Gauge**
– **Purpose:** Measures precipitation amount.
– **Functions:**
– **Accumulated Rainfall:** Tracks total rainfall over a set period.
– **Rainfall Intensity:** Quantifies precipitation per unit time.
3. **Rain and Snow Sensor**
– **Purpose:** Measures and counts rain and snow.
– **Operation:** It shows different kinds of rain and snow in different weather conditions. This information is useful for traffic systems and planning agricultural irrigation.
VI. Solar Radiation Measuring Devices
1. **Solar Radiation Sensor**
– **Purpose:** Measures total solar radiation or specific wavelength bands.
– **Operation:** It changes solar energy into electrical signals. It uses thermoelectric stacks or parts that run on solar power. This helps in solar energy production and climate studies.
2. **Ultraviolet Sensor (UV Index Meter)**
– **Purpose:** Detects ultraviolet radiation intensity.
– **Functions:**
– **UV Index:** Assesses UV levels for proper sun protection measures.
– **Outdoor Planning:** This provides details for planning activities. It also offers tips on how to keep your skin safe. It includes research about UV rays in the environment.
VII. Visibility Measuring Devices
1. **Forward Scattering Visibility Sensor**
– **Purpose:** Measures atmospheric visibility.
– **Operation:** The transmitter is tilted to send out light. This light works with particles in the air. The receiver detects how strong the scattered light is. This data measures three things: the scattering coefficient, the extinction coefficient, and how far we can see.
2. **Transmission Visibility Meter**
– **Purpose:** Calculates atmospheric visibility.
– **Operation:** It measures the average extinction coefficient of the air between the transmitter and the receiver. This helps find out how far we can see.
VIII. Weather Phenomena Measuring Devices
1. Weather Phenomena Meter
– Purpose: To find and evaluate different weather events.
– Features: This is a high-tech sensor system. It has a visibility meter, rain sensors, and tools to measure temperature, humidity, wind direction, and wind speed. By looking at these collected variables, it can determine specific weather conditions.
2. Lightning Locator
– Purpose: To find lightning strikes and measure their features.
– Features: This tool uses the sound, light, and electromagnetic field from lightning. It measures the details of lightning strikes from a distance. It sends processed lightning data in real-time to a central station.
There, more analysis is done. This device records important details such as the time, location, strength, direction, and other key signs of lightning activity.
IX. Integrated Weather Station
1. Integrated Weather Station
– Objective: To track and record different weather data completely.
– Capabilities:
– Multi-parameter Monitoring: This system watches several factors at the same time. It measures temperature, humidity, wind speed, wind direction, air pressure, and rainfall.
– Data Logging and Transmission: It stores past data and sends it through wireless or wired systems for more analysis.
– Automated Data Collection: This system lets us gather and share data in real-time. It uses automation technology to make sure the information is correct and up to date.
X. Specialized Meteorological Tools for Applications
1.Automated System for Observing Weather in Agriculture
– Purpose: “To watch crops and their surroundings in real-time.” This includes checking farmland and soil conditions.
– Features: This tool is made for specific farming needs. It collects information on small climate areas, soil conditions, and how crops grow. And it also gathers visual information, such as images or live video from farms.
It supports different power supply options. And it also talks to higher-level software using different ways to send information.
2. Traffic Weather Observation Station
– Objective: To provide quick and accurate monitoring of road and weather conditions.
– Features: This station works with systems that manage traffic. It helps create a smart traffic safety network.
And it checks important road conditions in real-time. It can find fog, ice on the road, and snow buildup. This helps make highways safer.
Summary
A wide range of weather measurement tools plays a key role in weather observation systems. These tools help us predict the weather correctly. They are useful for climate studies and many industries that rely on weather.
These tools help scientific research and weather services. They also help important areas such as farming, transport, and energy. This helps societies adjust to and use their environment better.
Modern weather systems use new sensors and technology to give accurate weather information. This helps people and businesses make smart choices using trustworthy data.