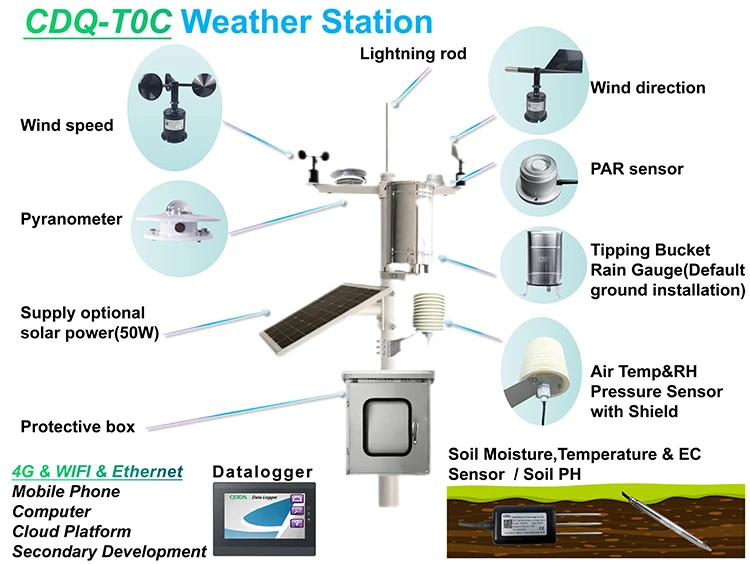
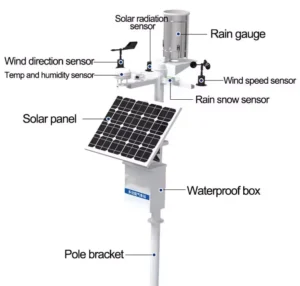
Industrial Weather Stations
Below is a comprehensive overview:
1. Defining an Weather Station
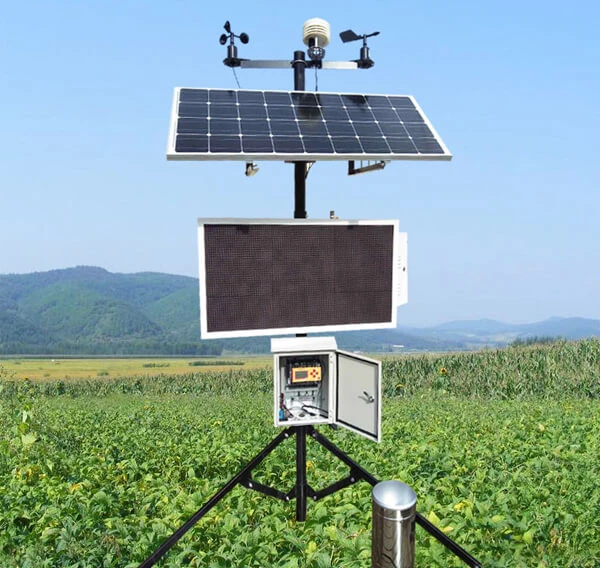
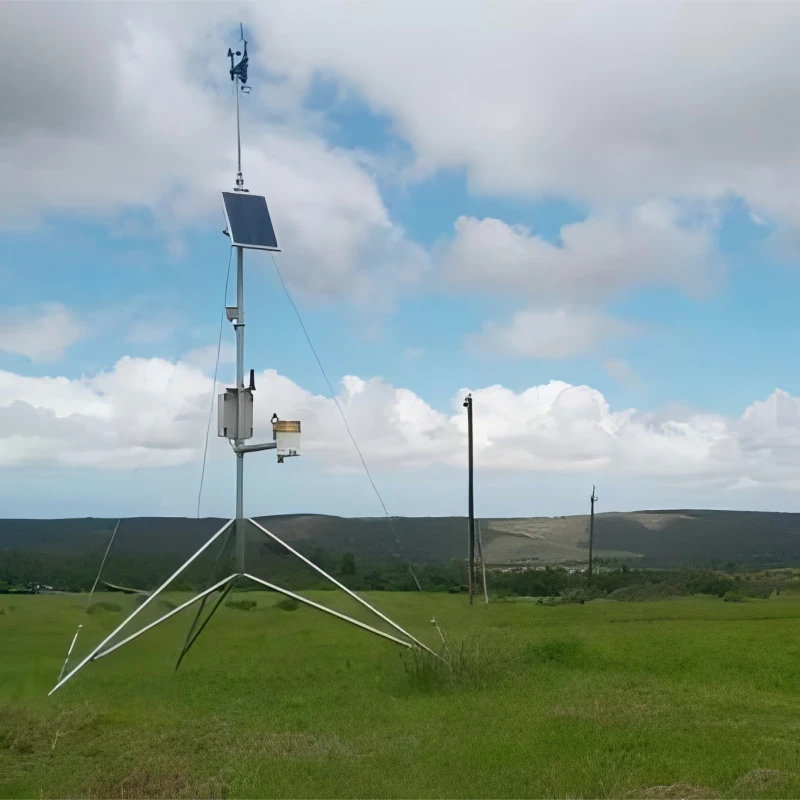
A professional industrial weather station is a facility that tracks weather in industrial areas. These stations are often near parks, chemical plants, and power stations. Their main job is to measure and record weather conditions and air pollution from industrial activities.
2. Sensors and Components of Weather Station
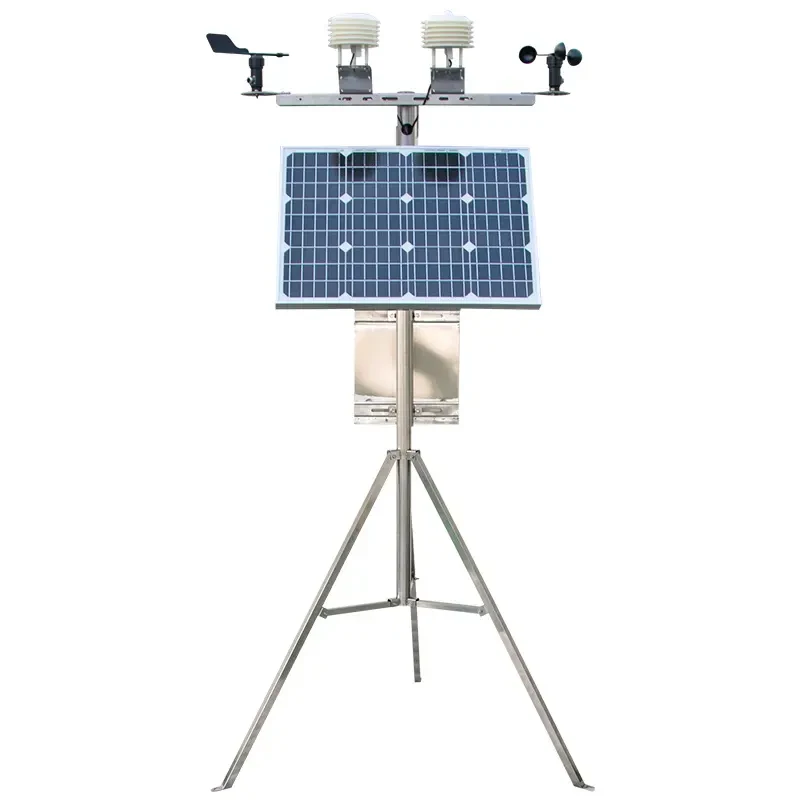
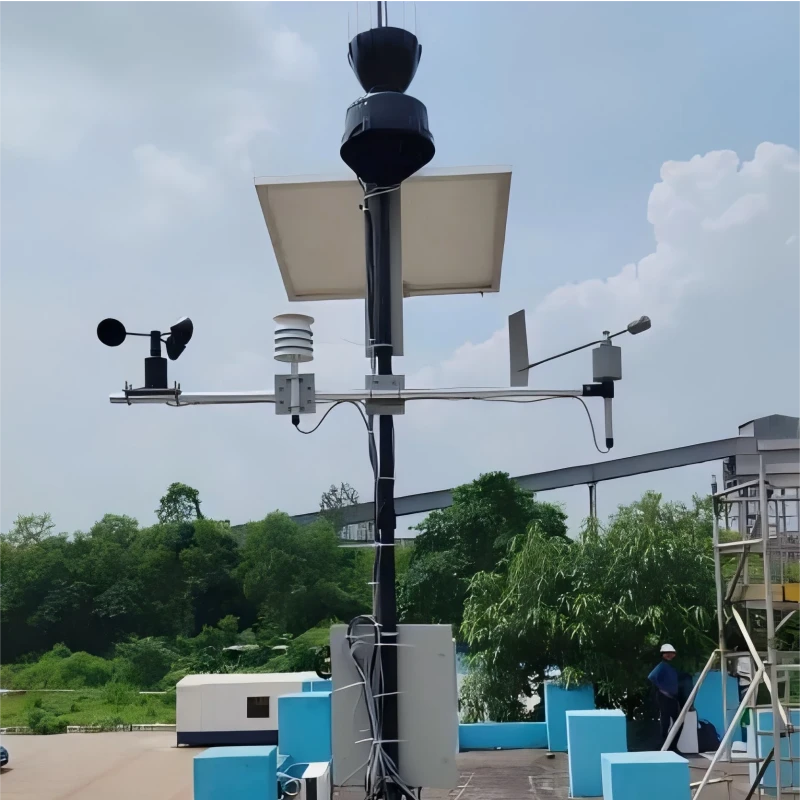
These professional weather stations are made for industrial use. They have advanced sensors and better data processing. The main sensors and key parts include the following:
Weather Sensors:
– **Temperature and Humidity Sensors**: “Measure the temperature and humidity to get accurate climate data.”
– **Barometric Sensors**: Check the temperature, humidity, and air pressure. These readings are important for weather forecasts and studying the atmosphere.
**Wind Speed and Direction Sensors**: Use hotwire or ultrasonic methods to measure wind speed. For wind direction, use wind vanes or magnetic systems.
– **Rain Sensors**: Detect rainfall levels.
– **Air Quality Sensors**: “Monitor particles like PM2.5 and PM10, as well as gases like SO2 and NOx.”
– **Harmful Gas Sensors**: “Measure gases like CO, H2S, and CH4. This helps keep people safe by finding harmful emissions.”
– **Solar Radiation Sensors**: Record solar energy levels.
Supporting scada systems and Components:
1. **Data Acquisition System**: Gathers sensor data and does the first processing.
2. **Data Transmission System**: This system sends data through wired connections like Ethernet. It also uses wireless networks like Wi-Fi, 4G, 5G, or satellite communication.
3. **Data Processing and Analyzing Software**: Analyzes data that has been collected, creates reports, and gives useful insights.
4. **Power Supply System**: It typically has a main power source and a backup system. This backup can be batteries or solar panels.
In areas where explosions might happen, some weather stations have special housings and connectors. This keeps them safe and stable in risky places.
RS485 or 4-20mA Output
RS485 Output:
Modbus RS485 is common in industrial communication. It has a long range and resists interference. The weather station’s data collector sends weather data to a computer or server. This is done through an interface for processing and analysis.
4-20mA Output:
This analog signal standard is often used in industrial control systems. Some sensors in weather stations use 4-20mA current signals. They send accurate weather data to connected devices.
Key Features of an Industrial Weather Station
1. **High Accuracy and Reliability**: Provides precise data required for crucial industrial decision-making processes.
2. **Weather Resistance and Durability**: Built to withstand tough industrial conditions, such as high or low temperatures, humidity, and corrosive environments.
3. **Versatility**: Monitors both standard Weather factors and industry-specific measures like dust, harmful gases, or radiation levels.
4. **Data Logging and Remote Transmission**: This allows for ongoing data recording. It also sends data in real-time to central control systems using network connections.
5. **Customizability and Integration**: Flexible to meet specific industry needs and able to work with larger systems like SCADA.
Industrial weather stations are important for safety. They help make industrial operations better and reduce harm to the environment.
Choosing the right industrial meteorological stations takes careful thought. You should think about different factors. This helps ensure they meet your current needs and future demands. Below is a simple guide to help you with the selection process:
1. Define Monitoring Needs
**Application Scenarios**: Identify the specific place for the weather station. This could be a petrochemical plant, a mining site, a factory, or a transportation hub.
**Monitoring Parameters**: List the environmental data to track. This includes temperature, humidity, wind speed, wind direction, barometric pressure, rainfall, PM2.5, PM10, and harmful gases.
– **Accuracy Requirements**: Decide how precise you need to be based on what you plan to do.
– **Data Logging and Transmission**: Decide if you need to log data. Choose how you want to send the data—wired or wireless.
2. Consider Environmental Conditions
– **Climatic Environment**: Test how well things can handle extreme conditions. This includes high or low temperatures, humidity, corrosive gases, and dust.
– **Installation Location**: Check how easy it is to access the installation site. Also, see if you need special mounting structures.
3. Determine the Budget
**Cost-Benefit Evaluating**: Keep track of your budget by watching your needs. Do a cost-benefit analysis to find a good price and performance balance.
4. Research Suppliers and Products
– **Supplier Reputation**: Choose reliable suppliers based on user reviews and case studies.
– **Product Certification**: Check that the weather station follows the right quality and safety standards.
– **Technical Support**: Check if suppliers offer technical support and maintenance services.
5. Compare Different Options
– **Feature Comparison**: – Check out different types of sensors.
– Look at their measurement ranges.
– Consider their accuracy levels.
– See how they store and send data in different models.
– **Durability**: “Look at how long products last and how well they hold up in tough industrial conditions.”
– **Expandability**: Choose systems that let you add or upgrade sensors as your needs change in the future.
6. Assess System Compatibility
– **Integration Capability**: Make sure the weather station can easily work with current industrial control systems like SCADA.
– **Data Format Compatibility**: Ensure that the weather station’s data output aligns with your current systems.
7. Evaluate Safety Features
Make sure the weather station is safe from explosions and can resist corrosion. It should work well in industrial settings.
8. Select Appropriate Data Transmission Mode
Pick a transmission mode based on distance, stability, and reliability. Your options are RS485, 4-20mA, Wi-Fi, and GPRS.
9. Consider Post-Maintenance Needs
Look for weather stations that are simple to install and care for. This will help reduce long-term costs.
10. Assess Installation and Operation
– **Ease of Installation**: Consider how complex the installation is and how much time it will take.
– **User-Friendly Operation**: Pick a system that is easy to use and take care of.
11. Request Quotations and Proposals
Work with suppliers to get clear quotes. These quotes should include costs for equipment, installation, training, and maintenance.
12. Conduct a Field Test (if Possible)
Whenever you can, do a field test to see how well the equipment works in real-life situations.
13. Make an Informed Decision
– Think about all factors before you decide.
– Check the technical details, cost, environmental impact, safety rules, and supplier support.
– After that, pick the best weather station for your needs.
Choosing the right industrial weather station needs a careful approach. You must balance technical needs, cost, and future upgrades. Making a smart choice ensures reliable monitoring. It also meets changing industrial demands.
Transmission Methods of Industrial Weather Stations
The way an industrial weather station sends data is important. It shows how information moves from sensors to a monitoring center. There are two main types of transmission methods: wired and wireless.
Wired Transmission
**Ethernet**: Offers a direct link to the network using an Ethernet cable. This is great for weather stations in fixed spots.
– **Serial Communication**: Uses interfaces like RS-232 or RS-485 for short-distance data transfer.
Wireless Transmission
– **Wi-Fi**: It sends information to a server that is close or far away using a wireless connection.
– **Cellular Networks**: Mobile networks like 4G and 5G are used for data transmission. This is helpful for remote or mobile monitoring.
– **Satellite Communication**: Satellite signals are used to send data. This is useful in remote or isolated areas. This method covers a large area and is not limited by distance. However, network stability and signal interference can affect it.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Transmission Method
– **Real-Time Data Requirements**: Check if real-time data transfer is important.
– **Geographic and Network Conditions**: Factor in the monitoring site’s location and available network coverage.
– **Data Security and Stability**: Wired connections are usually more stable. Wireless options might need better security measures.
– **Cost Implications**: Wireless methods often come with extra costs, like data plans.
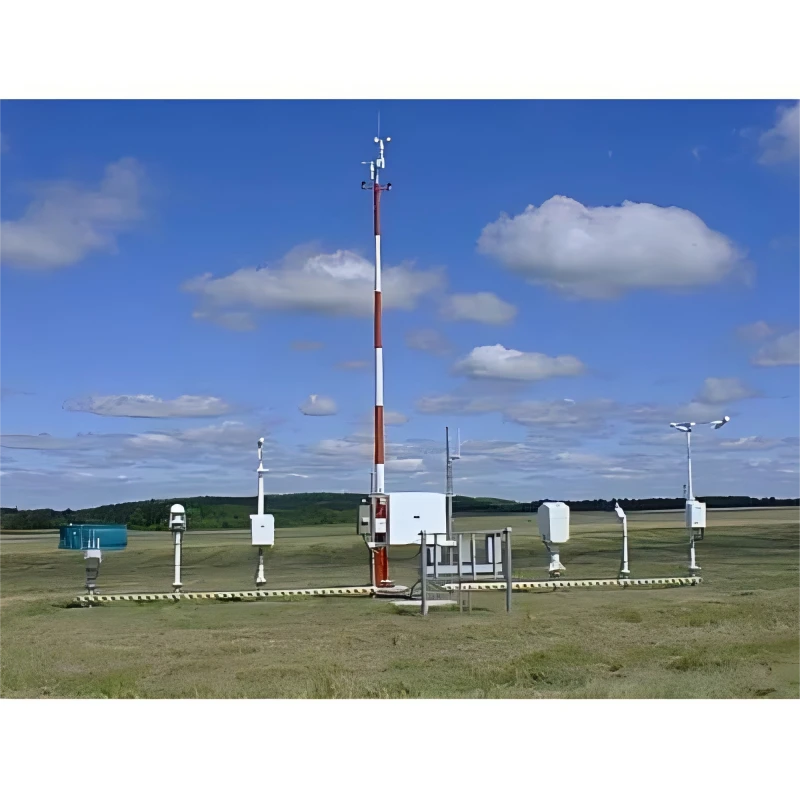
Installation Location Selection
Proper installation of industrial meteorological stations affects how accurate and reliable the data is. Here are some important things to think about when choosing a site:
1. **Meteorological Representativeness**
Select a site that truly reflects the weather conditions of the area you are studying. This will help ensure the data you collect is reliable and accurate.
2. **Safety Factors**
Place the station away from flammable or dangerous materials to keep it safe.
3. **Environmental Considerations**
– Limit direct sunlight to lower errors in temperature readings.
– Keep sensors away from pollution sources like chimneys and pipes.
– Consider wind barriers that may change wind speed and direction measurements.
4. **Accessibility & Maintenance**
– Choose a locati0n that makes it easy to do maintenance and calibration.
– Make sure there is enough space for installation and repairs.
5. **Structural Stability**
Make sure the locati0n and mounting setup can handle bad weather.
6. **Power Supply**
Make sure you have a reliable power source. If needed, look into other energy options like solar power.
7. **Data Transmission Requirements**
Check that the locati0n fits the hardware needs of the data transmission method, such as antennas or cables. By looking closely at these factors, you can ensure accurate data collection and long-term stability. This leads to a better monitoring system.
Application Scenarios of Industrial professional Weather Stations
Industrial weather stations are versatile. They serve many sectors, including:
– **Petroleum and Chemical Industry**: Keep an eye on harmful gas leaks to ensure safety at work.
– **Power Plants**: Track emissions like SO₂, NOₓ, and particulate matter to meet environmental rules.
– **Mining Industry**: Check gas levels in mines to stop explosions or poisoning.
– **Manufacturing Industry**: “Check indoor spaces to make production better and improve product quality.”
– **Transportation & Logistics**: “Watch the weather on roads and at ports to improve transport safety.”
Industrial Weather Station Price
The cost of industrial weather stations can vary for many reasons. These reasons include the brand, model, and features.
High-end brands usually provide better accuracy, stability, and reliability, but they cost more. On the other hand, budget-friendly options might not perform as well or last as long. Therefore, buying decisions should focus on your actual needs and budget. It’s important to think about both usefulness and cost.
When set up correctly, industrial weather stations give useful information to many industries. They help improve efficiency, safety, and compliance with regulations in different settings.