How Is Weather And Climate Data Measured?
Imagine a world where we can trust weather and climate information. This helps us make daily choices, like when to plant crops or when to leave before a hurricane. Without such essential data, life would be far more uncertain and perilous.
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) shows how important these measurements are. They report that better weather forecasting cut hurricane deaths by 86% from 1990 to 2015.
This shows how important it is to monitor weather and climate. It helps save lives, support businesses, and protect the environment.
Instruments Used in Weather Measurement
Understanding weather patterns and climate uses various tools to gather accurate and reliable data. Modern digital thermometers give accurate temperature readings. They can measure to a small fraction of a degree. They use either resistance or thermocouple technology.
Resistance thermometers measure how the electrical resistance of metals, like platinum, changes with temperature. Thermocouples measure changes in electrical potential between two different metals. Both methods provide accurate and reliable temperature readings.
Humidity is measured with hygrometers. These devices check how much moisture is in the air. This is important for farming, building materials, and different environmental conditions.
Capacitive hygrometers measure changes in capacitance when moisture comes into contact with a conductive material. In contrast, resistive hygrometers check changes in resistance as dampness affects absorbent materials.
Wind speed is measured with anemometers. These tools are important for predicting bad weather and assisting with offshore wind farms. There are three types of these devices: cup, propeller, and sonic.
Cup anemometers have rotating cups on a shaft. The shaft spins when the wind blows. This gives direct speed readings.
Propeller anemometers measure wind speed by the rotation of their blades. Sonic anemometers use sound waves to get accurate readings of wind speed and direction.
Barometers are important tools for tracking changes in air pressure. They show trends that can warn us about changes in the weather. Mercury barometers measure pressure by the height of a mercury column. Modern aneroid barometers use metal bellows or diaphragms.
These are often paired with electronic systems for continuous monitoring. This setup provides real-time readings. A sudden drop in air pressure often means a storm is coming.
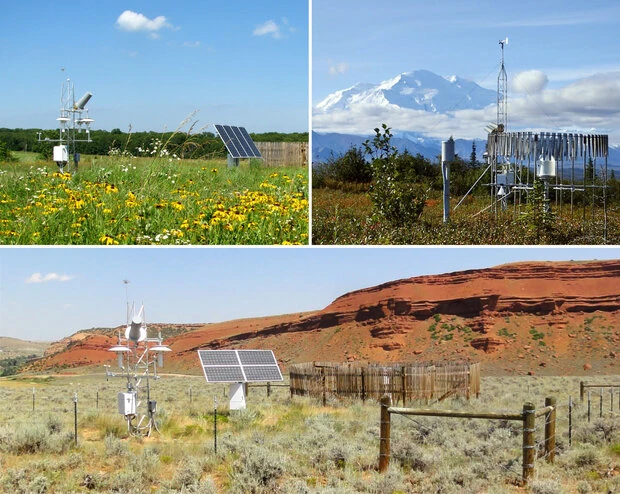
Homemade weather stations provide local information about climate conditions. They use simple tools like thermometers, hygrometers, wind vanes, and anemometers.
These setups help track local weather trends. They can spot temperature drops that signal cold fronts. These cold fronts may bring rain or snow.
Satellite Technology and Remote Sensing in Climate Measurement
Satellites equipped with advanced sensors play a critical role in monitoring varied atmospheric and surface characteristics. Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) in NASA’s Terra et Aqua satellites, exempli gratia, colligit notitias de temperie, vegetatione, et colore oceani. This detailed information is important for studying climate change. It helps track long-term trends in plant health and ocean temperatures.
MODIS has played a key role in showing the decline of Arctic sea ice. This decline is an important sign of global sea levels and changing climate systems. The VIIRS is on the Suomi NPP satellite.
It gives accurate data about clouds. It also provides information on sea surface temperatures. This information is important for understanding weather patterns and predicting climate changes. VIIRS data is very helpful for spotting new tropical storms and tracking hurricane paths.
The CALIOP instrument on the CALIPSO satellite studies aerosol and cloud properties. It gives important information about Earth’s atmosphere and its impact on climate.
Large events like El Niño and La Niña affect global climate. We can monitor them well using satellite data. However, despite their benefits, satellites face challenges such as calibration errors, equipment degradation, and cloud interference, which can affect data accuracy.
Checking satellite information with ground-based measurements is still very important. Ground stations, especially in remote or high areas, are important for checking satellite observations.
Ground-Based Observatories and Weather Stations
Ground-based observatories and weather stations are placed in key locations. They help fill the gaps in weather and climate monitoring.
These facilities excel in gathering detailed local data on weather conditions. A weather station on a mountain provides important information about high-altitude climates. This helps with aviation safety and mountaineering.
Meteorological stations usually work for national weather services, universities, or private companies. They carefully collect data on temperature, humidity, pressure, wind patterns, and rainfall. Programs such as the Global Climate Observing System (GCOS) and the World Weather Watch (WWW) gather data consistently worldwide.
This standardization helps scientists study climate trends over long periods, including decades and even centuries. A well-known example is the Mauna Loa Observatory in Hawaii. It has measured carbon dioxide levels since 1958. These measurements show how human activity affects the climate.
Advancements in Weather Forecasting and Climate Modeling
Modern weather forecasting is much better now than old methods like pendulums and barometers. Today’s weather forecasts depend a lot on numerical weather prediction (NWP) models. These models use advanced methods to analyze weather conditions with data from observations. We use variables like temperature, humidity, wind speed, and pressure to predict future weather patterns.
The Global Forecast System (GFS) makes detailed forecasts with high resolution. The Community Climate System Model (CCSM) looks at long-term climate trends and their wider effects.
Climate modeling looks at many factors. It includes ocean currents, ice movements, and human actions like deforestation and urbanization. This helps us understand long-term changes related to climate shifts.
Recent advancements include using machine learning in forecasting tools. This has improved accuracy in predicting extreme weather events and changing climate impacts. Even with these improvements, weather forecasting is not perfect. This is because of possible errors in data and limits in computing.
Consequently, efforts to refine forecasting methods persist. These include optimizing algorithms in NWP models and boosting the resolution of simulation tools. Advances in computer technology and better data collection methods have greatly improved forecasting accuracy. This makes short-term weather predictions and long-term climate models more reliable.
Challenges and Constraints in Weather and Climate Measurement
It is important to calibrate equipment correctly for accurate results. Over time, if instruments are not calibrated correctly, they may drift. This can cause wrong measurements. Regular checks and adjustments are important to keep data accurate.
Other factors like sensor wear, data handling errors, and human mistakes can affect accuracy. This shows the need for backup systems. We should use different tools and check data from various sources.
Regional differences make things more complicated. Weather and climate systems change a lot in different areas. The Arctic has unique challenges because of its cold climate, thick ice, and many clouds.
These factors can make it hard to collect data from satellites. It is important to combine ground-based observatories with satellite observations. This helps us collect local data and build a full global picture.
Advancing Knowledge in Weather and Climate
Using new ideas and different data so,.urces helps us create a more flexible and sustainable future. This future can better address climate challenges.
Measuring weather and climate accurately impacts many areas. This includes daily forecasts and long-term climate research that lasts decades.
Tools and methods, like thermometers and spacecraft, provide important insights into how Earth’s climate works. To understand these systems better, we need to improve how we measure them. We should also combine different datasets.
This method helps us understand global climate patterns better. It also helps people take informed actions to deal with environmental change. We are making ongoing improvements in technology and methods. These will help us better deal with the challenges of changing climate conditions.