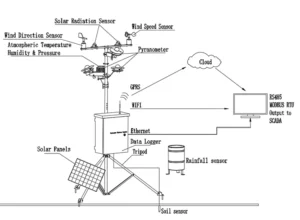
how does an anemometer work
Anemometer function: An anemometer is a tool that measures the speed of the wind. It is often used in weather science, environmental studies, aviation, and more. This article explains how an anemometer works and what it does.
**Working Principle of an Anemometer**
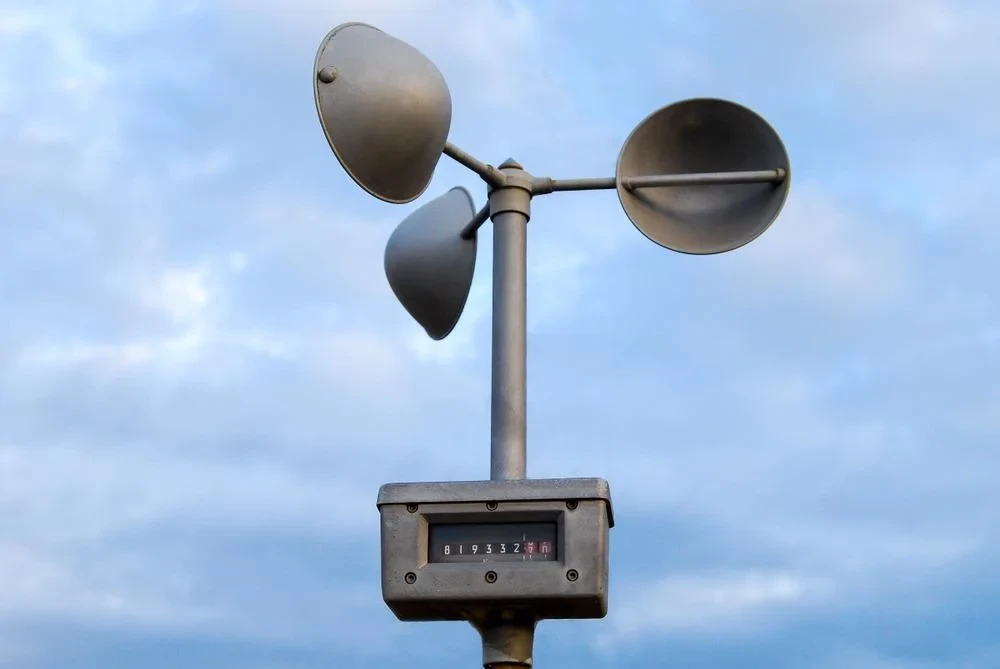
The main idea of an anemometer is to measure how the wind pushes on an object. This helps us find the wind speed. The simplest type of anemometer is mechanical.
It often has blades that look like fans. These blades are at a right angle to the wind. When the wind blows over these blades, it makes a force. The strength of this force depends on how fast the wind blows.
This force makes the blades spin. We can read the speed of these blades directly. We can also use a device to change it into speed of the wind.
With new technology, anemometers now come in different types. These include electronic, sonic anemometer,tube anemometers, and hot wire types of anemometers. All the methods are different, but they all measure how wind interacts with objects.
anemometer uses
Anemometers are tools that measure how fast the wind blows and which way it is going. They can also do other tasks based on different needs.
– **Real-time Monitoring**:
Anemometers provide real-time data on changing wind speeds. This feature is important in many fields, such as weather, aviation, and protecting the environment.
For example, weather departments use data on wind speed and direction to make better forecasts. Aviation authorities change flight speed and altitude based on this data to ensure safety. Environmental agencies use this information to check air quality and watch pollution levels.
– **Data Recording**:
Many cup anemometer can measure wind speed over time. This makes them helpful for long-term studies in weather and environmental science. This data helps weather scientists look at climate trends. It also helps experts learn how pollution spreads.
– **Alarm System**:
Advanced models often come with alarm features. These alerts let users know when wind speeds are too high or too low. These warnings help users act quickly. In wind farms, operators can automatically stop the turbines.
They do this if wind speeds get too low. This stops energy waste and keeps the equipment safe.
– **Data Transmission**:
Modern sonic anemometer often send data. This allows them to connect easily with computers or cloud platforms. Users can store, analyze, and check data from a distance. It also makes it easier to share the data with key stakeholders.
In summary, anemometers are useful tools for accurately measuring speed. They are important in many fields. Knowing how they work shows their value and flexibility in many uses.
As science and technology advance, we expect mechanical anemometer to get better. This will make them more helpful in the future.