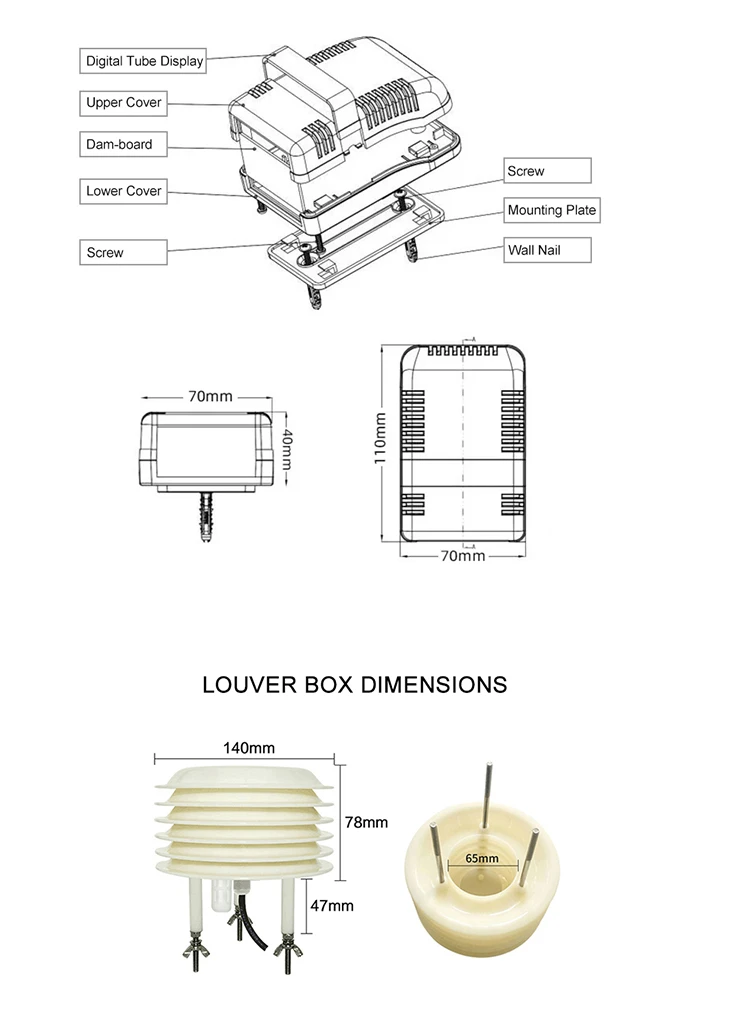
Difference between PM2.5 sensor and PM10 sensor
It is important to know the difference between PM2.5 and PM10 sensor. This knowledge helps you choose the best tools to check air quality. Here is a summary of their features, functions, and uses:
**Introduction to PM2.5 Sensors and PM10 Sensors**
PM2.5 sensors find small particles in the air. These particles are 2.5 microns wide or less. These tiny particles can go deep into the lungs or get into the bloodstream. This can cause serious health risks.
PM10 sensors find particles that are as small as 10 microns wide. These are known as respirable particles. They mainly affect the upper part of the breathing system.
**Operating Principles**
PM2.5 sensors often use laser or infrared light to check air quality. Laser models emit laser light to scatter particles.
The strength of the scattered light helps us find out how many particles are present. Infrared sensors use LED lights and special detectors to work. They check how much light bounces back.
PM10 sensors use lasers to find particles in the air. This means that light scattered by particles helps measure concentration levels.
**Impact on Health**
PM2.5 particles are more harmful to health than PM10 particles. Their smaller size allows them to enter the lungs more easily. This can impact the heart and blood vessels.
This can lead to heart and lung diseases. PM10 particles are harmful. They mainly affect the upper parts of the respiratory system. Their effects are often less severe.
**Advantages and Disadvantages**
PM2.5 sensors are good at finding small changes in air quality. They are sensitive to small particles. This makes them more accurate as technology gets better.
Smaller particles are harder to remove. This has a strong impact on human health.
PM10 sensors are accurate and reliable. They are easier to clean because they track larger particle sizes. They may not notice small changes in air quality as well as PM2.5 sensors do.
**Common Applications**
PM2.5 sensors are great for indoor places like homes and offices. They are also useful in air quality monitoring stations. These sensors can accurately detect fine particles.
PM10 sensors are often used outdoors. You can find them in weather stations, factories, libraries, and places that need to check dust levels.
**Measurement Range**
Both sensor types usually measure from 0 to several hundred micrograms per cubic meter, such as 1000 µg/m³. These sensors usually meet various monitoring needs, even though the products can differ. Choosing between them depends on the particle size and concentration you need for your needs.
**Price Comparison**
The cost difference is due to the need for sensitivity and accuracy. PM2.5 sensors often cost more than PM10 sensors. This is because PM2.5 sensors can detect smaller particles.
Prices vary a lot. Basic sensor modules cost around $50. High-precision models with advanced features can cost more than $500. The real cost depends on the brand and the product’s technical details.
conclusion
PM2.5 and PM10 sensors play different roles in air monitoring. They can find particles of different sizes. These particles can have various effects on health. Their functions and uses are also different.
Choosing the right sensor depends on the environment. It also depends on how precise you want the monitoring to be. Knowing these differences helps us make better choices for managing air quality.