Comparison of Wireless Communication Modules
Wireless communication modules are key for IoT devices. They help these devices send information over the Internet. These modules act as a gateway for smart devices to connect to the Internet of Things (IoT). They form a key connection between the IoT perception layer and the network layer.
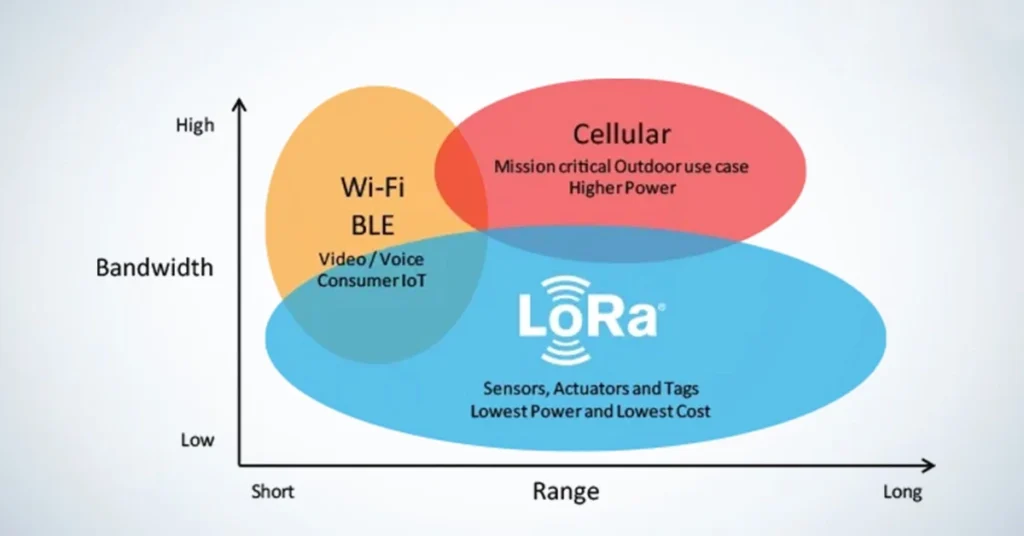
Right now, cellular communication modules such as 2G, 3G, and 4G are common in Machine-to-Machine (M2M) situations. In the next few years, many people will likely start using low-power wide-area network (LPWAN) modules. This includes technologies such as NB-IoT and LoRa.
Wireless communication modules gather data from IoT devices. They then send this data to the network layer. This lets you control devices from afar using cloud management platforms. It also helps with quick data analysis.
These modules make management more efficient in various situations. They are a key hardware part for IoT terminals. Each module connects straight to its terminal.
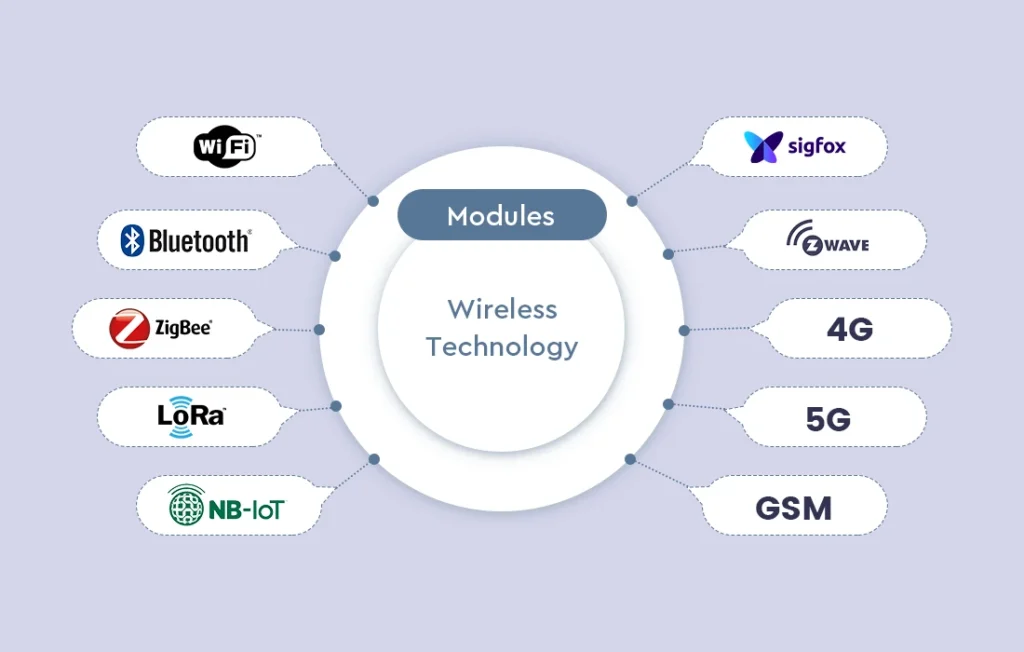
There are many types of wireless communication modules on the market. It’s important to know how they are different. These technologies are made to meet specific situations and user needs. Here is a summary of key wireless communication modules:
Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a very common wireless technology we use every day. This standard allows short-range data exchange between fixed and mobile devices. It works in personal area networks. It uses radio waves in the 2.4 to 2.485 GHz range.
– High complexity in technology.
– Device connection typically takes around 10 seconds.
– High integration and reliability.
– Data transmission rate of approximately 1 Mbps.
– Low cost and easy installation.
Bluetooth stands out as a suitable technology for short-distance wireless communication.
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi is a common wireless technology that many people use every day. The IEEE 802.11 standard allows wireless local area networking. It does this by changing wired signals into radio wave signals. Devices connect with a wireless module for easy use.
– Coverage usually extends up to 100 meters.
– Transmission rates can go up to 54 Mbps.
– Operates on a 2.4 GHz frequency band with transmission power below 100 mW.
Wi-Fi is useful for many things because it is easy to find. However, its data security is not as good as Bluetooth’s.
ZigBee
ZigBee is a low-power network protocol. It is based on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard. This standard was introduced in 2001. The technology had many problems when it first came out. It has been improved and is now a trusted standard for industrial use.
– It is like Bluetooth but fixes its problems. And it uses less power and has a longer range.
– This system is made for strong industrial automation. It is easy to set up, resists interference, provides reliable transmission, and is low cost.
– Communication can reach from a few meters inside to many hundreds of meters outside.
Traditional Digital Radio
Digital radio means high-quality systems for sending data. These systems use digital signal processing and wireless technology that is defined by software. There are good ways to communicate in complex fields like fiber optics and microwaves.
– Able to send data over long distances at a speed of 19.2 Kbps.
– High terminal costs and operational expenses.
– Installation needs more technical skills than other wireless modules.
In summary, different wireless communication modules are made for specific needs and situations. They offer various features like range, power use, speed, and cost. They form the backbone of connection in our connected world. This is especially true with the rise of IoT applications.