What is conductivity in water?
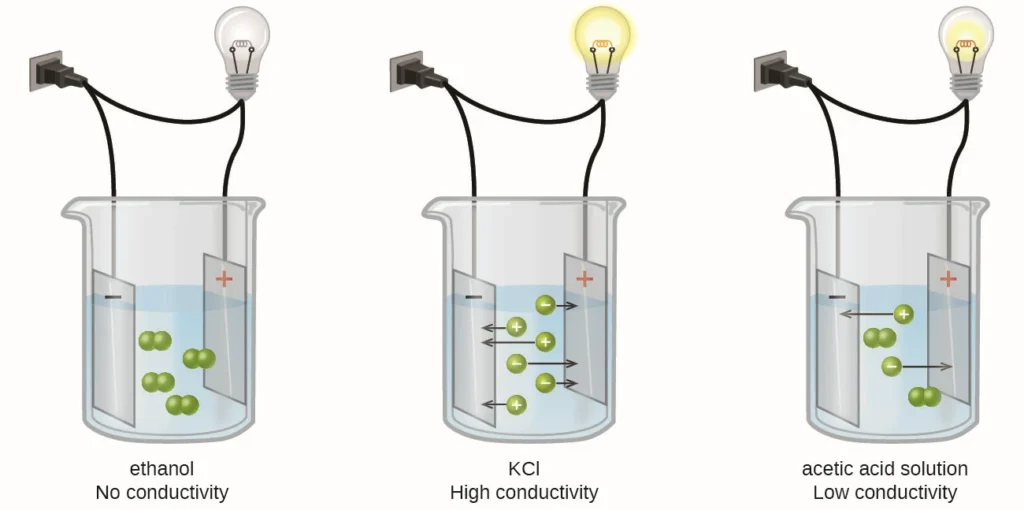
Conductivity in water is how well it can conduct electricity. This ability mainly depends on the amount of dissolved electrolytes. Electrolytes are compounds that break into free-moving ions when mixed with water. These ions help electricity flow.
There are positive and negative ions. When the amount and type of electrolytes increase, water conducts electricity better. Other factors, like temperature and pressure, can also change conductivity. However, pressure has little effect in normal conditions.
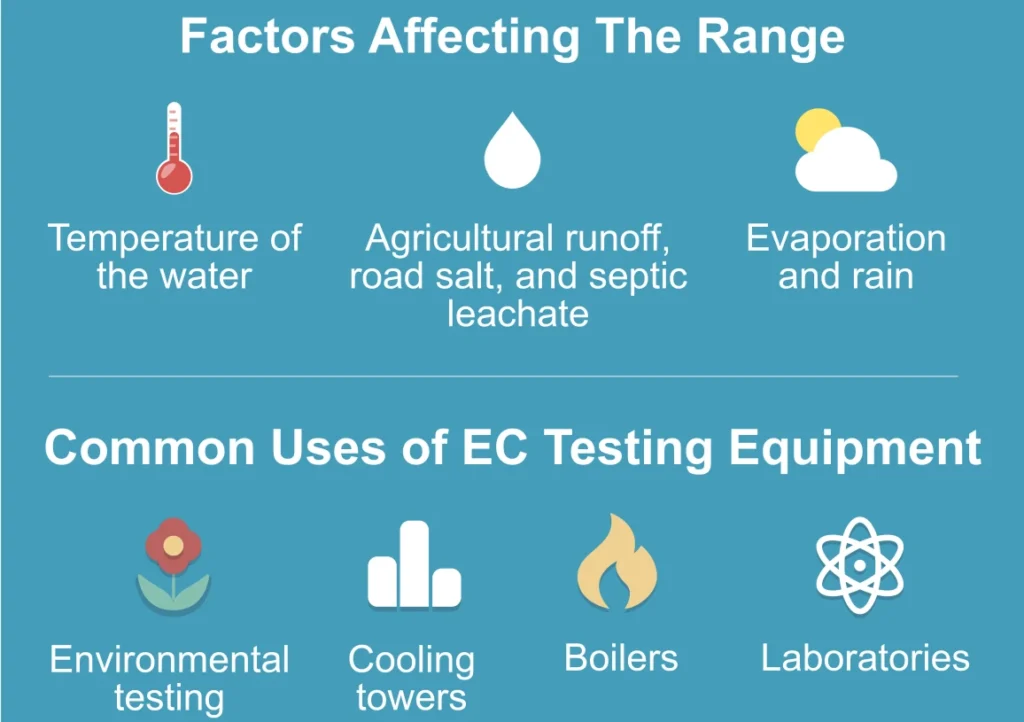
**Factors influencing the magnitude of conductivity in water**
The conductivity of natural water mainly depends on the number and types of ions present. Temperature is important because ion movement increases with heat. The effect of pressure is small unless measurements are taken in deep water. For most field tests, pressure changes can be ignored.
**Why is conductivity in water important?**
Conductivity is a key way to check water quality. It shows how well water conducts electricity. This helps us know what ions are in the water.
Pure water has very few free-moving ions. Because of this, it does not conduct electricity well. In contrast, seawater has many ions that conduct electricity well. This high conductivity helps us measure ocean health and the state of marine life.
Conductivity is linked to salinity, which shows how much salt is in water. We cannot measure salt directly, so we use conductivity tests to estimate salinity and total dissolved solids. This information helps us understand aquatic habitats. Salinity affects dissolved oxygen levels, which impacts the living conditions of aquatic species.
Conductivity values can warn us about changes in water quality. When conditions are stable, the conductivity of most water sources stays the same. This consistency can be a baseline for future comparisons.
Big changes in conductivity may indicate natural events like flooding or evaporation. They can also show harmful pollution from humans, which can harm ecosystems. Regularly checking conductivity is important for managing water quality issues.
**What causes high conductivity in water?**
– **Presence of ions:** Conductivity happens when charged ions in water move due to an electric field. Pure water has few ions, so it has low conductivity. However, gases like carbon dioxide can raise conductivity when they dissolve in water. This process creates ions, like hydrogen carbonate, through chemical reactions.
– **Higher electrolyte concentration:** More electrolytes lead to more free-moving ions in water. This makes water conduct electricity better.
Adding different amounts of salt to the same amount of pure water shows a clear result. More salt means higher electrolyte levels. Higher electrolyte levels lead to higher conductivity.
**Types of ions affecting conductivity**
Different ions can conduct electricity in different ways. Water with electrolytes breaks down into ions that help it conduct better. For example, salts dissolve into ions that conduct electricity well. This is why salty water, like seawater, is much more conductive than pure water, which has very few ions.
Temperature has a big effect on water conductivity. When the temperature rises, conductivity usually goes up too. This is because higher temperatures allow ions to move more easily. For every 1°C increase in temperature, water conductivity goes up by 2-4%.
This effect happens because ions move faster at higher temperatures. Also, salts and minerals dissolve better when it’s warmer.
What does high conductivity in water signify?
High conductivity means there are more dissolved salts, minerals, and possibly pollutants in the water. Checking these levels helps us know what ions are present. In nature, rain can wash minerals from the soil into rivers. This process raises conductivity.
On the other hand, human activities like farming, industrial waste, and pollution can raise conductivity levels by adding contaminants. However, high conductivity does not always mean bad water quality. It may just show a higher amount of harmless dissolved electrolytes that do not harm health.
Is it better to have lower water conductivity?
Water conductivity shows how many dissolved substances are in water and how they affect electrical flow. Pure water has low conductivity, around 50 µS, because it has few ions. When ions like sodium, calcium, and magnesium dissolve, conductivity levels go up.
In nature, water conductivity changes a lot based on geography and soil type. For example, river or lake water usually has a conductivity between 100 and 1000 µS. In contrast, seawater or very salty industrial water can have conductivity values in the thousands of Siemens (S).
Conductivity does not define water quality by itself. It is only one of many factors used to assess it.
For example, adding sugar and salt can make water more conductive. But this does not mean the water is harmful. Also, water with low conductivity is not always safe from toxic substances.
To fully check water quality, we need more tests. This includes using tools like pH sensors and turbidity meters.
Applications of conductivity measurement:
1. **Assessing Water Purity**
Measuring conductivity is important for checking how pure water is. Pure water has few ions and shows low conductivity.
In contrast, seawater, salty solutions, or dirty water have more ions. This leads to higher conductivity. So, measuring conductivity is a good way to assess water purity.
2. **TDS (Total Dissolved Solids) Reference**
Conductivity is a good way to estimate how much salt is in water. When salt, mostly sodium chloride, dissolves, it makes sodium and chloride ions. These ions increase the water’s conductivity. This measure is helpful in desalination, farming, food production, and other fields.
3. **Industrial Water Monitoring**
Industries check the conductivity of cooling water, boiler water, and process fluids to keep things running smoothly. Monitoring conductivity in real-time helps detect changes in water quality. This allows for quick actions to prevent damage from corrosion or scaling. It also helps maintain efficiency and safety in production.
4. **Environmental Monitoring**
In environmental protection, we measure the conductivity of natural water sources. This includes rivers, lakes, and oceans. It helps us check the quality of the water.
Continuous monitoring can show pollution trends or contamination events. This helps us analyze and act quickly to protect the environment. These measurements give us important data to manage and preserve aquatic ecosystems effectively.
How to Measure Conductivity in Water?
1. **Conductivity Electrode**
The conductivity electrode method is a common way to measure how well water conducts electricity. It works by placing an electrode in the water. The ions in the water interact with the electrode.
This interaction makes a small electric current. The strength of this current shows how many ions are in the water. This helps us find the water’s conductivity.
This method is good for measuring things in real-time. However, water temperature and impurities can change how the electrode reacts. This can cause errors. To keep accuracy, regular calibration and proper maintenance are very important.
2. **Conductivity Test Paper**
This method uses conductivity test paper, which is like pH paper. It provides an approximate reading of conductivity. Users can compare the paper’s color change to a standard color chart. This helps them estimate the conductivity level.
This method is simple to use, but it is not very accurate. It works best for quick checks in emergencies or for casual home use. The test paper does not last long and needs to be replaced often. This makes it not great for long-term monitoring.
3. **Water Conductivity Sensor**
Conductivity sensors offer a precise and automated way to measure water conductivity. These sensors use advanced tools to continuously check conductivity levels. Often, they are part of control systems, providing accurate and stable results.
This makes them helpful in many places. They are often used in wastewater treatment systems. There, they work with other sensors. These include pH, dissolved oxygen, and turbidity sensors to check water quality.
4. **Remote Sensing Measurement**
Remote sensing uses satellites or planes to check water quality from a distance. This method can quickly gather data over large areas. However, its accuracy can be affected by factors like water clarity and color.
Also, remote sensing equipment is expensive and needs regular maintenance. This limits its use, even though it is fast and covers a lot of ground.