What is Optical Sensor
In today’s world of advanced technology, optical sensors are very important in many industries. They change how we see, measure, and interact with our surroundings. But what is an light sensor? It is a tool that finds light signals.
It measures these signals and converts them into electrical signals. You can use this data for further processing and analysis. This article will explain how ambient light sensors work. It will cover their types, uses, and future trends.
Working Principles
At the center of an optical sensor is how light interacts with matter. When light hits an object, the object’s properties can change.
These properties include light intensity, wavelength, polarization, and phase. Designers make photoelectric sensors to detect light these changes. They then turn the changes into useful information.
An optical sensor has three main parts: a light source, a sensing element, and a detector. The light source sends light to the object or area you want to measure. The sensing element can be a light-sensitive material, a fiber optic probe, or a small optical structure.
It interacts with light and changes based on what is measured. This can include temperature, pressure, distance, or how much of a chemical there is. The detector picks up the light signal and changes it into an electrical signal. An electronic circuit then processes this signal to give you the measurement result you need.
For example, in a basic light sensor, the light source sends out a beam of light. When the light hits an object, some of it bounces back to the detector. The amount of reflected light depends on the object’s surface and how far it is from the sensor.
The detector checks how strong the light that bounces back is. It then changes this light into an electrical current or voltage. The sensor studies the electrical signal. It can tell if the object is present.
It can also measure how far away the object is. It can also find out how much the object reflects.
Types of Optical Sensors
Optical sensors can be classified into different types. This classification is based on how they work and what they are used for.
Photoelectric Sensors
Photoelectric sensors are a common type of optical sensor. They work on the photoelectric effect. This effect happens when light hits a material that can sense light. This makes electrons come out, which creates an electrical current.
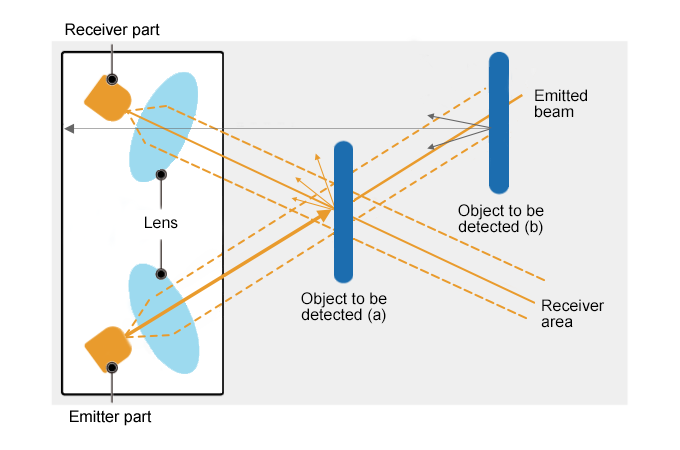
You can divide photoelectric sensors into three types: through-beam, diffuse reflective sensors, and retro-reflective sensors. Through-beam probes have one part that sends signals and another part that gets them. They detect objects by interrupts a light beam between them.
Diffused reflective probes find light that bounces off an object. Retro-reflective sensors use a reflector to send light back. These probes are used in factories, robots, and security systems. They help find objects, count things, and sense where they are.
Fiber Optic Sensors
Fiber optic sensors use optical sensing fibers to sense things. These fibers can send light far with little loss. They are not affected by electromagnetic interference. This makes them great for harsh environments and remote sensing.
Fiber optic sensors can measure a wide range of physical quantity of light, such as temperature, pressure, strain, and chemical concentration. In a fiber optic temperature sensor, the fiber’s refractive index changes with temperature.
This change affects how converts light moves through the fiber. By measuring device these changes in the light signal, we can find the temperature accurately. Fiber optic sensors are often used in aerospace, oil and gas exploration, and medical diagnostics.
Spectroscopic Sensors
Spectroscopic sensors look at how light interacts with matter at different wavelengths. Each substance has a unique spectral signature. This signature helps us find and measure the substance.
Spectroscopic sensors include UV-Vis spectrometers, IR spectrometers, and Raman spectrometers. Researchers use these tools to study chemicals. They also look at the environment and test how good the food is.
An IR spectrometer can find specific chemical bonds in a sample. It measures how much infrared light is absorbed at certain wavelengths. This helps find pollutants in the environment and check food products.
Applications of optical sensors
Optical sensors are used in many ways. This has led to their wide use in different fields.
Industrial Automation
In manufacturing plants, photoelectric sensor play a vital role in quality control, process monitoring, and automation. They help find where parts are on a production line. They check the size of parts and see if they are put together correctly.
For example, photoelectric probes can find items on a conveyor belt. They can start actions like sorting, packaging, or checking quality.
Fiber optic sensors can check the temperature and strain of machine parts. They provide early warnings of possible problems. This helps avoid costly downtime.
Healthcare
In the medical field, photoelectric sensors help with tests and monitoring. They are used for procedures that do not need surgery or only need small cuts. Pulse oximeters use these probes to check the oxygen level in the blood. They do this by looking at how hemoglobin absorbs light conditions in different colors.
Optical fibers are used in endoscopy. They send visible light to brighten organs inside the body. They also send images back to the surgeon.
Scientists are creating sensors to find diseases early. These probes check the chemical makeup of body fluids or tissues. They help find cancer.
Environmental Monitoring
Optical sensors are important for watching the environment. They check the quality of air, water, and the weather.
Spectroscopic probes can find pollutants in the air. These pollutants are sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and small particles.
Fiber optic sensors measure temperature, pH, and dissolved oxygen in water. They give us important data to protect the environment and manage water resources.
In weather monitoring, photoelectric sensors are used in devices like pyranometers and ceilometers. Pyranometers measure solar cells convert. Ceilometers measure the height of clouds.
conclusion
Optical sensors are an interesting and quickly changing technology with many uses. They can find and measure light signals very well. This makes them important in today’s technology.
As research goes on, optical sensors will become more important in many industries. They will also help make our lives better.