Functions, Working Principles and Applications of Soil pH Sensors
Farmers use soil pH sensors as smart tools to check soil pH levels. Measuring soil pH is key for plant growth. Farmers can use this information to change the soil’s acidity or alkalinity. This helps boost crop growth and yield.
This article will explain what soil pH sensors are. It will explain how they work and where they are used.
Part 1: What is a soil pH sensor?
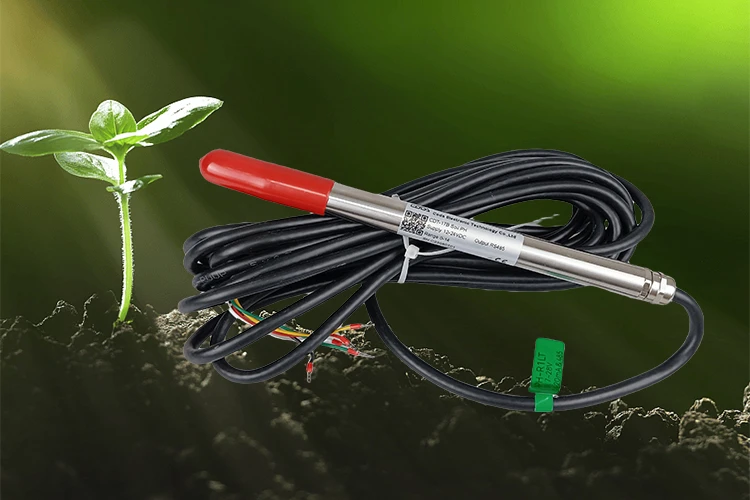
A soil pH sensor is a tool that measures the pH levels of soil. It detects hydrogen ions (H+) in the soil with electrodes. The pH level shows the amount of hydrogen ion activity present. This shows if the soil is acidic or basic.
The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14. Values below 7 show acidity. Values above 7 show alkalinity. This sensor detects pH levels from 0 to 14. It sends an electrical signal that matches the pH level.
The sensor turns these readings into electrical signals. It sends them to users or farm management systems for quick checks and evaluation.
part 2: Operational principles of soil pH sensors
The soil pH sensor works through chemical reactions. It mainly measures how electrodes work and changes signals.
Measurement of Electrode Potential: The sensor has two parts. One is a reference electrode, and the other is a sensing electrode. The reference electrode keeps a steady potential compared to the sensing electrode.
When the sensor is put in a soil solution, it creates a difference in voltage between the two electrodes. This voltage difference relates to the number of hydrogen ions in the soil solution. This shows the pH level.
Signal Change: The electrodes make a change in voltage. This change turns into an electrical signal that is simple to measure. This signal usually shows up as voltage or current, which relates to the pH level.
The sensor may also have parts like amplifiers and filters. These parts help make pH measurements accurate and reliable.
Uses of Soil pH Sensors in Agriculture
1. Soil acidity regulation:
Soil pH sensors help farmers track changes in soil pH levels. This allows them to take quick action when needed. By changing the soil’s acidity or alkalinity based on these readings, farmers can create better growing conditions. This helps plants grow strong and healthy.
2. Fertilizer management:
Different crops need different soil pH levels. Farmers can use a soil meter to check if the soil is acidic or alkaline. This helps them use fertilizers based on the needs of each crop.
This method helps avoid using too much or too little fertilizer. This helps increase both the amount and quality of crops.
3.Soil enhancement:
Soil pH probes help farmers see how acidic or alkaline the soil is. They can make the soil better by adding organic matter, lime, and other materials. Checking soil pH levels often helps keep the soil healthy.
4. Pest and disease management:
Some pests and diseases need specific soil pH levels. Farmers can use soil pH sensors to quickly change how acidic or alkaline the soil is. This helps reduce the risk of pests and diseases. It also lowers the need for pesticides, which is better for the environment.
Other uses of soil pH sensors
Environmental monitoring: Soil pH probes are used to check soil quality and its effects on ecosystems. They help find soil acidification or alkalization caused by pollution or human activities. These sensors show the health of the soil.
Pollution control: Soil pH probes are important for controlling pollution. They can detect changes in the pH levels of the soil. These changes may show that harmful substances or chemicals are present. They help locate polluted areas and track the progress of cleanup efforts.
Academic research uses soil pH sensors to study how pH levels impact soil microorganisms. It also looks at nutrient cycling and plant growth. These sensors provide important data for understanding soil acidification and its impact on the environment.
Conclusion:
Soil ph meter are important tools in farming, environmental studies, and pollution control. They are key parts of smart farming devices. These sensors assist farmers by measuring how acidic or alkaline the soil is.
They help improve crop yield and quality. This allows for better fertilization and pest control. It also helps with sustainable farming. Knowing how they work helps us understand soil acidification and alkalization.
This knowledge can help make farming better and support land use that lasts.