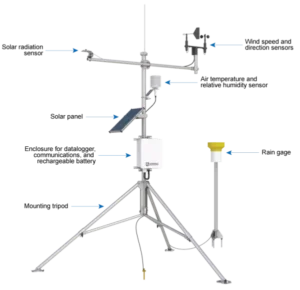
How do 2D anemometers differ from 3D anemometers?
A 2D anemometer, also called a 2D ultrasonic wind sensor, measures the horizontal parts of wind speed and direction.hat is the difference between 2D and 3D anemometers?
The difference between 2D and 3D anemometers is in what they can measure and how they are used. Both tools measure how fast the wind blows and which way it goes. However, they differ in size, complexity, and how they are used.
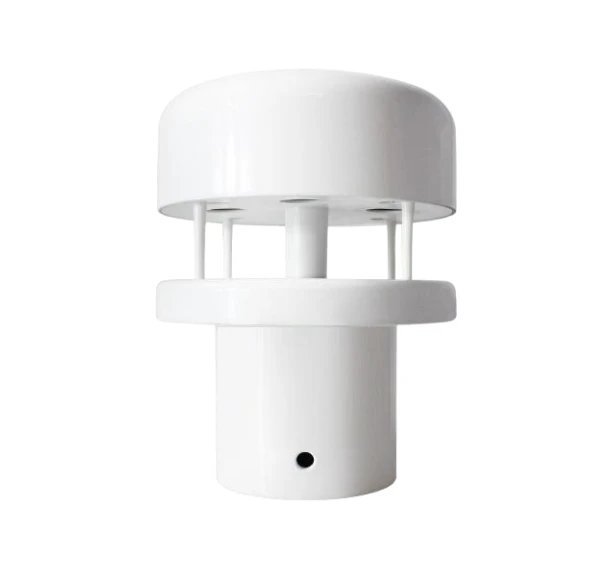
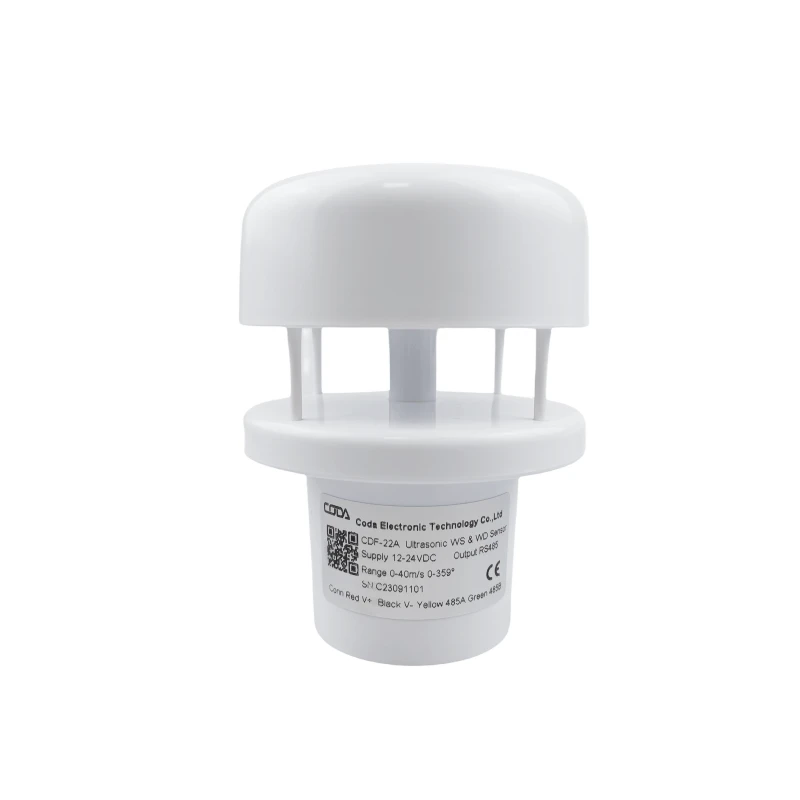
**2D Anemometer**
A 2D anemometer, or 2D ultrasonic wind sensor, measures the horizontal speed and direction of the wind. It works with ultrasonic waves.
The speed of these waves changes based on how fast the wind blows. It checks the arrival time or changes in the waves. This helps it find the wind speed and direction.
Key characteristics include:
– Measure wind in a horizontal direction.
– Send data using analog or digital signals.
– High accuracy makes it good for different weather conditions.
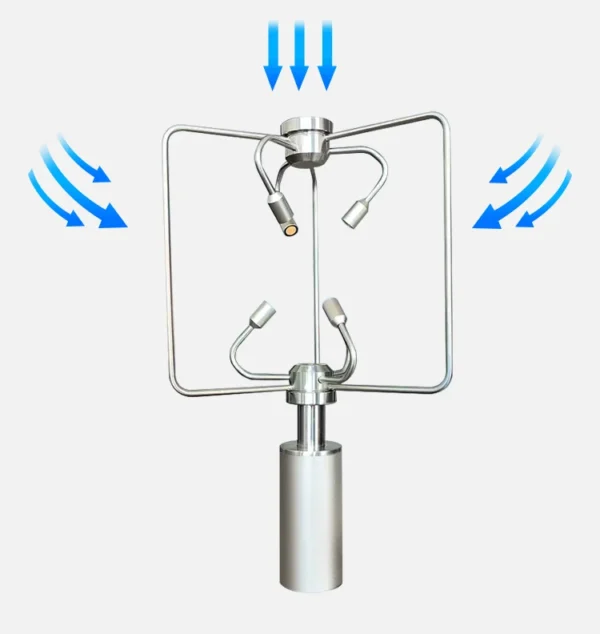
**3D Anemometer**
A 3D anemometer measures how fast the wind blows and which way it goes. It does this in three dimensions at the same time. And it is also known as a 3D ultrasonic anemometer.
It uses ultrasonic technology to measure wind components (u, v, w) on three axes. This gives data on the total wind speed and direction at any moment.
Primary features:
– Measures wind in three ways.
– High sensitivity, good resolution, and stable performance for long-term observations in the field.
– Good for analyzing pulsations and advanced research.
Application Scenarios:
**Uses of 2D Anemometers:**
– **Meteorology:** Weather stations or satellites collect wind data.
– **Transportation:** Wind information helps planes land and helps vehicles find their way.
– **Agriculture:** Farmers look at the weather to find the best time to plant.
– **Construction:** We check how wind affects buildings.
– **Marine Activities:** We watch wind direction and speed for sailing and navigation.
**Uses of 3D Anemometers:**
– **Meteorology:** Tracking wind changes in three dimensions for better forecasts and research.
– **Environmental Protection:** Watching how pollutants move in the air helps us make better choices.
– **Construction:** We test wind pressure and vibrations with wind tunnel experiments.
– **Scientific Research:** Studying vertical wind components in methods like vorticity correlation.
– **Wind Power Generation:** Evaluating wind resources to improve where turbines are placed.
Summary:
Both 2D and 3D anemometers are helpful tools. They measure how fast the wind blows and which way it goes. Each one has special benefits based on how it is designed.
A 2D anemometer works well when you do not need to measure vertical wind. A 3D anemometer is best for areas that need a close look at wind patterns. Choosing the right device depends on what the user needs and their budget.