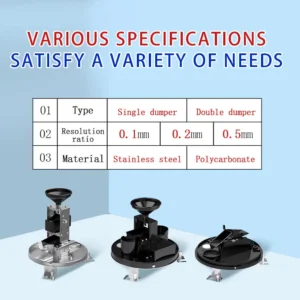
What Is a Digital Anemometer Used For?
In a world where air wind flow impacts weather and industry, the digital anemometer is a key tool. A digital anemometer measures how fast the wind blows. It can also show which way the wind is blowing. Its accuracy and flexibility make it important in many fields, from science to daily life.
Understanding the Basics of a Digital Anemometer
Before we look at its uses, we need to understand how a digital anemometer works. Digital anemometers are not the same as traditional ones.
Traditional anemometers have parts that move. These include cup anemometers, wind vane anemometers, and tube anemometers. They check how fast the wind is blowing.
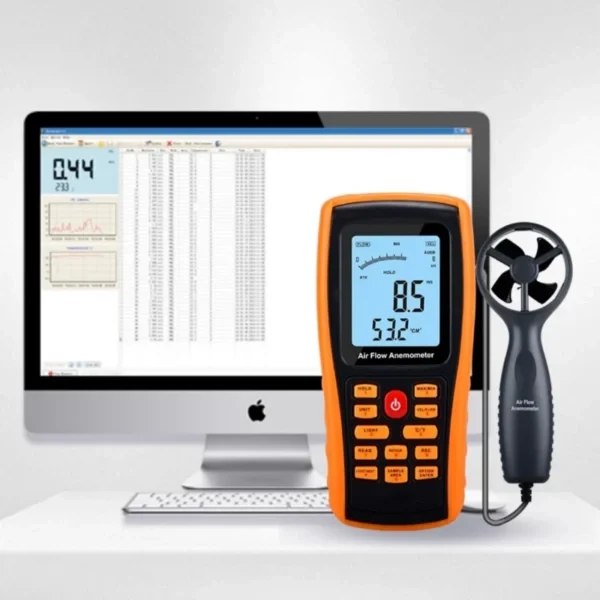
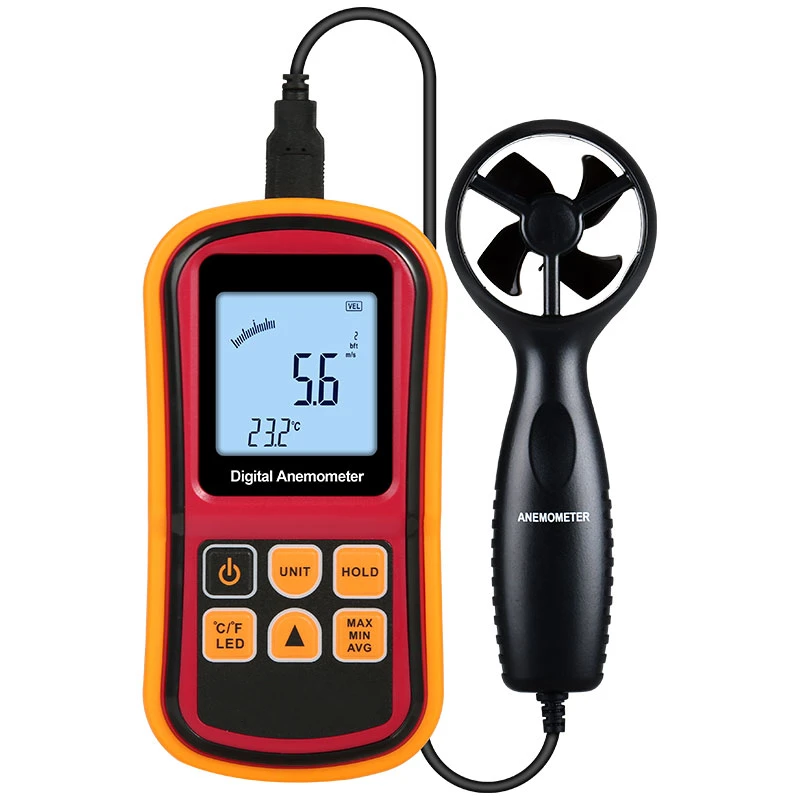
In contrast, digital anemometers use modern technologies. These include ultrasonic sensors, hot wire anemometer, and pressure sensors. A sonic anemometer measures how fast the wind is blowing. It does this by timing how long sound waves take to move between sensors.
The calculations for wind speed and direction use changes in the travel time of these sound waves. Hot-wire type of anemometer real time measure wind speed by sensing how air cools a heated wire.
As the wind blows over the wire, it cools it down. A stronger wind cools the wire more quickly. This change can be seen on a digital display.
Weather Forecasting and Climate Research
A key use of digital anemometers is in weather forecasting. Meteorologists use these tools to gather wind data from many places around the world. By tracking wind speed and direction, they can better understand and predict weather patterns.
Strong and steady winds can indicate that a storm is on the way. Sudden changes in wind patterns may mean a new weather front is forming. People use digital anemometers on weather balloons, ships, and weather stations that are far away. These tools give important data that helps make weather models and forecasts more accurate.
In climate research, digital anemometers play a vital role in studying long-term wind patterns. Scientists gather data for many years to see how wind conditions change. They look at seasons, climate changes, and different locations.
This information helps us understand how the Earth’s atmosphere works and how climate changes happen. For example, changes in wind patterns can change ocean currents. These changes can also impact climate systems all over the world.
By measuring air wind speed and direction, researchers can learn more about these links. This information helps us make better plans for dealing with climate change.
Aviation and Aerospace Industries
In aviation and aerospace, flight safety and efficiency depend on precise wind data. Digital anemometers are used on planes. They measure wind both on the ground and in the air.
During takeoff and landing, pilots rely on anemometer readings. These readings help them know about headwind, tailwind, and crosswind.
Headwinds make the aircraft need more distance to take off but help with braking when landing. Tailwinds do the opposite. Strong crosswinds can be a big challenge for pilots. They can cause the aircraft to drift off the runway.
With good wind speed and direction, pilots can change their flight paths and speeds. This keeps the journey safe and smooth.
In the aerospace industry, digital anemometers help test and develop aircraft and spacecraft. Wind tunnels with precise anemometers create different wind conditions. This helps study how aerodynamic designs work in various airflow situations.
This helps engineers make better shapes for aircraft and spacecraft. It cuts down drag and improves fuel efficiency. Anemometers also check airflow around launch pads. This makes sure rockets can launch safely, even in strong winds.
Marine and Offshore Operations
Digital anemometers are useful tools for work done at sea. They help keep ships and platforms safe when they are at sea. On ships, anemometers check the direction and speed of the wind. This helps captains make good choices about navigation, speed, and routes.
Strong winds can make large waves. These waves can make a ship less stable and harder to steer. If captains know the wind conditions in advance, they can stay away from dangerous areas. They can also change the ship’s path to lessen the impact of rough seas.
In offshore work, such as oil and gas drilling, workers use digital anemometers. These tools measure the wind close to platforms. Strong winds can put workers and platforms at risk. Anemometer data helps start safety measures when wind speeds go above certain levels.
This can mean moving parts workers or stopping work to prevent accidents. Accurate wind measurements are important for making offshore wind farms work better. Operators can look at the wind patterns in the area. This helps them put wind turbines in the right spots to make more energy.
Industrial and Environmental Monitoring
In factories, power plants, and ventilation systems, digital anemometers are used to measure airflow. Good air circulation is key for a healthy and productive workplace.
Anemometers help technicians and engineers check how well ventilation systems work. They can find blockages or issues. This helps them make changes that improve air quality.
In a factory, measuring the speed airflow accurately can stop harmful fumes or dust from building up. This keeps workers safe and helps them follow safety rules.
In environmental monitoring, digital anemometers help study how pollutants spread in the air. Scientists check how fast the wind blows and which way it goes. This helps them predict how pollutants move from sources like factories, power plants, and cars. This information is key for making plans to lower air pollution and protect public health.
Anemometers are used in forestry to study wind patterns. They help understand how wind affects forest fires. Knowing wind conditions helps firefighters predict how fires will spread and plan better firefighting strategies.
In conclusion, the digital anemometer is a helpful and important tool. It has many uses in our lives.
They help make air and sea travel safe. They make industrial processes better and help protect the environment. As technology gets better, we can expect more accurate digital anemometers. This will help us measure and understand the complex world of wind.