CO2 Sensors: Definition, Types, and How to Choose
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a key indicator for assessing indoor air quality. However, unlike some other pollutants, CO2 is colorless, odorless, and imperceptible to the human senses. The only reliable way to determine CO2 levels indoors is through the use of CO2 sensors.
What Is a Carbon Dioxide Sensor?
A carbon dioxide sensor is a device that detects gas. It measures how much CO2 is in the air. When CO2 levels deviate significantly—either becoming too high or too low—the sensor triggers an alert. This lets people act quickly based on the sensor’s readings. This helps keep air quality within safe levels. These sensors are useful in everyday life and in industry. They help create a healthier and safer atmosphere.
Types of CO2 Sensors
There are many types of CO2 sensors on the market. Each one is made for different uses and needs. To choose the best sensor for your needs, you should know the benefits and limits of each type. Here’s an overview of four commonly used CO2 sensors, categorized by their working principles:
1. Non-Dispersive Infrared (NDIR) CO2 Sensors
NDIR sensors operate based on the principle that different gases absorb infrared light in unique ways. The sensor features an internal infrared lamp that emits light at a fixed wavelength. When carbon dioxide is present, it absorbs specific bands of this light, causing changes in the infrared signal. The system handles this change in several steps. First, it filters the data. Then, it amplifies it. After that, it converts the data from analog to digital (ADC). Next, it adjusts for temperature and pressure. Finally, the microprocessor calculates the CO2 concentration.
**Advantages:**
– High sensitivity
– Rapid analysis
– Excellent stability
– Long lifespan
**Disadvantages:**
– High power consumption
– Complex design (hardware and software)
– Relatively expensive
2. Electrochemical CO2 Sensors
Electrochemical sensors use chemical reactions to convert CO2 concentrations into electrical signals. You can group them into potential, current, or capacitive types based on the signals they detect. They use either liquid or solid electrolytes. Among these, solid electrolyte sensors have gained significant research focus since the 1970s. These sensors create an electric force by generating ions from gas. They measure this force to find CO2 levels.
**Advantages:**
– Fast measurement
– Easy operation
– Low cost
**Disadvantages:**
– Short lifespan
– Susceptible to aging and “drifting” over time
– Influenced by other gases, reducing measurement accuracy
3. Semiconductor CO2 Sensors
Semiconductor sensors depend on oxidation-reduction reactions between CO2 and the sensor’s semiconductor surface that change the resistance of the sensing material. When gas touches this surface at a steady temperature, it sticks to the surface. This process causes chemical changes that affect electrical conductivity. These sensors can use MOS diodes or field-effect transistors to detect CO2 levels, depending on their design.
**Advantages:**
– Quick response time
– Strong resistance to environmental factors
– Stable structural design
**Disadvantages:**
– Easily affected by temperature and humidity fluctuations
– Better suited for high or uncommon CO2 concentrations
– Interference from other airborne substances
4. Catalytic Combustion CO2 Sensors
Catalytic combustion sensors use a specific catalyst coated on a resistor to measure CO2 concentrations. At elevated temperatures, CO2 combusts catalytically on the sensor’s surface. For this reason, people also refer to these as thermal combustion sensors.
**Advantages:**
– High measurement accuracy
– Quick response time
– Extended service life
**Disadvantages:**
– Limited to certain gas types within its detectable range
7 Types of CO2 Sensors Used in Different Environments
Carbon dioxide (co2 molecules) sensors come in various forms to suit specific applications and environments. Besides differing in their working principles, designers tailor their designs and functions to meet diverse needs. Below are seven types of CO2 sensors and their typical uses:
**1. Home CO2 Meters**
Home co2 gas meters are small, practical, portable, and wireless. They help monitor indoor levels of carbon dioxide, temperature, and humidity. These devices play a vital role in evaluating the bedroom’s microclimate, ensuring optimal living and working conditions. Equipped with user-friendly electronic screens, they provide actionable information to help improve indoor air quality.
For office use, these sensors can help keep team productivity high. They are easy to use, affordable, and do not need wiring.
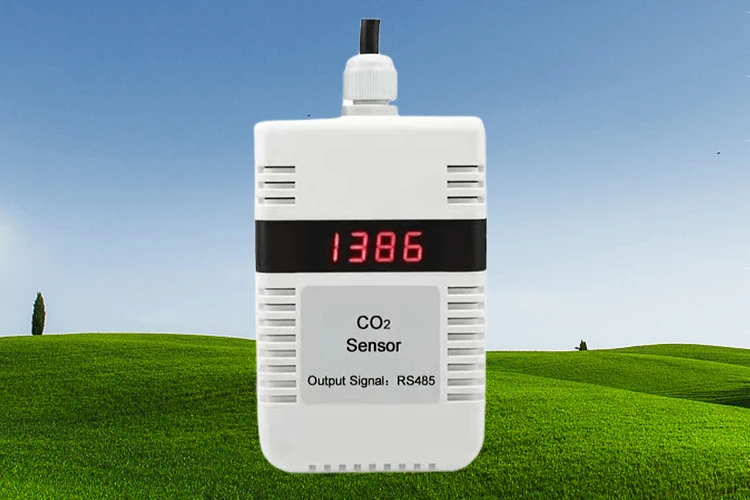
**2. Wall-Mounted CO2 Sensors**
Wall-mounted sensors are very durable and professional-grade. They work well in places with high levels of co2. These places include schools, offices, hotels, greenhouses, and factories. These devices often measure co2 levels from 0 to 5000 ppm or 0 to 10,000 parts per million ppm. Designers make them with waterproof casings. This allows them to work well in tough conditions for 5 to 10 years after they are installed.
These sensors typically use RS485 or analog outputs to deliver stable and precise data readings.
**3. Portable CO2 Detectors**
Portable CO2 detectors are versatile tools for mobile measurements in varying locations. These detectors are small and battery-powered. They can work for up to 8 hours straight. This makes them perfect for professionals who need real-time data on the go. The devices have a clear display and an alarm system. This alerts users when CO2 levels go above safe limits.
**4. Fixed CO2 Detectors**
Fixed CO2 detectors are made with safety in mind. They are explosion-proof and fire-resistant. This makes them essential for dangerous places that may have flammable or explosive conditions. Their robust stainless steel construction ensures protection against water and dust. Installed permanently in industrial settings, these detectors can transmit measurement data remotely, reducing risks and enhancing safety by preempting dangerous incidents.
**5. Outdoor CO2 Sensors**
Outdoor applications demand sensors that can withstand exposure to the elements—rain, snow, extreme temperatures, and UV radiation. CO2 sensors with IP68-rated protection endure such conditions while maintaining optimal functionality. Their anti-corrosion housing lets fresh air flow in while keeping water out. This ensures reliable data for long-term outdoor co2 monitoring. Users can also access this data remotely for added convenience.
**6. All-In-One CO2 Sensors**
To get a comprehensive view of environmental air quality, a multi-parameter sensor is often needed. All-in-one CO2 sensors do more than just measure carbon dioxide gas. They also track temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, light intensity, and other gases. These gases include carbon monoxide, ammonia, methane, oxygen, formaldehyde, total volatile organic compounds, ozone, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen dioxide. Some advanced models can simultaneously measure up to 11 elements without interference between them. This multifunctional approach eliminates the need for multiple devices in broad air quality assessments.
**7. Duct-Type CO2 Sensors**
Duct-type sensors are specialized devices used to monitor CO2 concentration inside ventilation or HVAC systems. A stainless steel probe mounts the sensor and inserts it into a duct through a pre-drilled hole. This design allows accurate long-term measurement in confined spaces airflow paths while being simple to install and operate.
Each of these types serves a unique purpose based on the environment that monitors it, helping maintain safety, productivity, and air quality across various sectors.