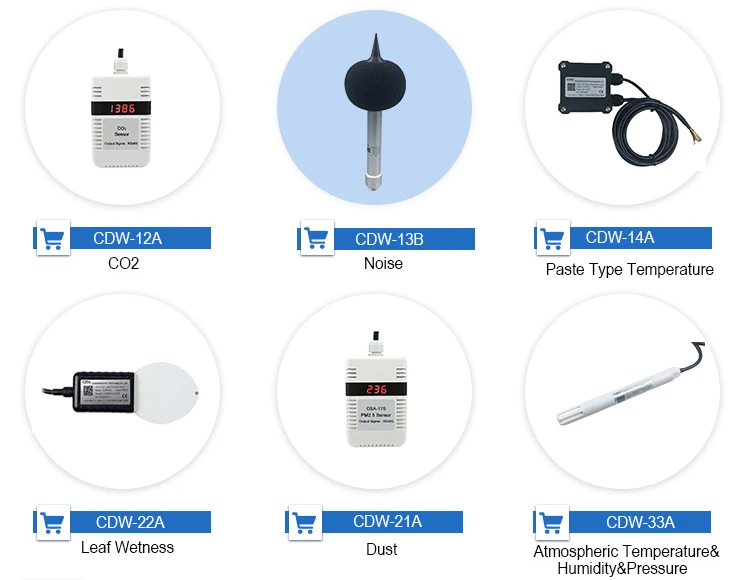
Sensors for Environmental Monitoring
Environmental monitoring sensors are instruments designed to assess and track environmental parameters, gathering data pertinent to the environment. These devices employ a variety of techniques and principles to identify and quantify different environmental factors. Below, I elaborate on several typical environmental monitoring sensors and their underlying principles in detail.
1. Temperature Sensors
These devices are employed to gauge the environmental temperature. Typical examples include thermocouples, thermistors (such as NTC and PTC), and infrared sensors.
Thermocouples work by using the thermoelectric effect between two different metals. This creates a voltage that helps measure temperature by looking at voltage changes. Thermistors assess temperature by observing changes in their resistance as temperature fluctuates. Conversely, infrared sensors determine temperature by detecting the infrared radiation emitted by an object.
2.Humidity sensors
Assess the moisture levels in the surroundings. Typical types include capacitive, resistive, and surface mount humidity sensors. Capacitive humidity sensors operate on the principle of capacitance variation and determine humidity by observing the change in capacitance as moisture absorbs. In contrast, resistive humidity sensors gauge humidity by examining how moisture affects resistance.
3. Barometric Sensors
These sensors are designed to evaluate atmospheric pressure. Common varieties include piezoresistive and capacitive sensors. Piezoresistive sensors determine barometric pressure by detecting changes in the resistance of the piezoresistive element as atmospheric pressure varies. Meanwhile, capacitive sensors assess air pressure by measuring alterations in capacitance.
4. Light sensors:
These devices are utilized to assess the brightness level in the surroundings. Typical light sensors encompass photoresistors, photodiodes, and phototransistors. Photoresistors gauge light intensity by altering resistance when exposed to light. Photodiodes and phototransistors transform light energy into electrical signals, functioning based on the photoelectric effect principle.
5.Researchers use gas sensors
To detect the levels of gases in the environment. These gases include carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, methane, and volatile organic compounds. Common gas sensors consist of electrochemical, infrared, and semiconductor types.
Electrochemical sensors determine gas concentration through the chemical reaction that takes place between the gas and an electrode. Infrared sensors measure how much gas absorbs infrared light at a certain wavelength. This helps determine the gas concentration. Semiconductor sensors evaluate gas concentration by observing the change in electrical resistance when the gas interacts with the semiconductor material.
6. Soil Moisture Sensors:
These devices are employed to assess the water content within the soil. Among the typical types are capacitive and resistive sensors.
Capacitive sensors determine moisture levels by evaluating the variation in capacitance between the soil and an electrode. Resistive sensors measure moisture by checking how the soil’s conductivity changes. This change depends on the soil’s moisture level.
7.Water quality sensors
Monitor different factors in water. They check pH levels, dissolved oxygen, conductivity, and turbidity. Typical water quality sensors include electrochemical, optical, and conductivity varieties.
Electrochemical sensors evaluate water quality by detecting changes in the chemical potential within the water. Optical sensors determine water quality by analyzing the absorption, scattering, or transmission characteristics of light. Conductivity sensors gauge water quality by measuring the conductivity of the water body.
These environmental monitoring tools can connect to data logging systems or cloud platforms. This allows for real-time data transmission and storage. It also helps with data analysis, visualization, and application. This facilitates a deeper understanding and management of environmental conditions, thereby enhancing environmental quality and promoting sustainable development.
Sensors for environmental monitoring are crucial in a variety of application scenarios, with their primary uses and benefits outlined below:
1.Weather prediction and climate studies:
Sensors to measure temperature, humidity, and atmospheric pressure. You can find these sensors in weather stations and meteorological satellites. They collect data on atmospheric conditions.
This data is important for predicting weather changes. It helps provide accurate weather information. This is crucial for weather forecasting, disaster alerts, farming, and climate research.
2.Monitoring air quality:
Sensors detect toxic gases present in the atmosphere. These gases include carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, and methane. This is important for checking air quality in cities, managing pollution from industries, and improving indoor air quality. It helps us understand and improve air quality to protect health.
3.Monitoring water quality:
Sensors track different factors in water. These include pH levels, dissolved oxygen, conductivity, and turbidity. This is crucial for safeguarding water sources, ensuring the safety of drinking water, protecting aquatic ecosystems, and conducting environmental assessments. These sensors enable the timely identification of water quality issues, allowing for the implementation of appropriate corrective actions.
4. Management in agriculture and horticulture:
Soil moisture sensors help check soil moisture levels. They assist farmers and horticulturists in improving irrigation and fertilization schedules. This leads to better crop yield and quality. It also reduces water waste and environmental pollution.
5. Energy Efficiency Management in Buildings:
Sensors measure temperature, humidity, and light. They help track energy use and save money in buildings. By tracking indoor conditions in real-time, you can improve air conditioning and lighting control. This helps save energy and reduce costs.
6. Monitoring of Industrial Production Processes:
Sensors for temperature, humidity, and air pressure are utilized for overseeing and controlling industrial production processes. Continuous observation of environmental factors guarantees a consistent production setting, upholds product standards, and reduces production mishaps and losses.
Smart home systems and IoT applications use sensors for temperature, humidity, and light. Tracking indoor environmental parameters allows for automatic adjustments to indoor temperature, humidity, and lighting, which enhances quality of life and promotes energy conservation.
Environmental monitoring sensors are important in many areas. They help people understand and manage the environment. These sensors protect health, increase productivity, save resources, and support sustainable development.