how to install weather station ?
We should think carefully about different factors for install weather station. First, we need to choose sites based on the geography and needs. Second, we should consider the types of transmission methods.
Wired Ethernet gives stable connections but can be limited by where you are and high costs. The 4G network covers a large area. This makes it easy to set up in many places. To find out how to install a weather station, keep reading this article.
We need to make sure the data acquisition equipment connects to devices like computers, smartphones, and tablets using WIFI. This will help receive and process data. We should think about how bad weather might impact the signal and transmission.
Selecting the Location:
When you set up a accurate weather station, pick a large and open space. Such an area needs to be far away from all kinds of obstructions like buildings, trees or other edifices. Nearby obstacles could change normal wind measurements. They may also impact the accuracy of temperature readings and humidity readings.
The chosen spot for the weather station must match the area around it. It should not have heat sources or too much moisture. These factors can change the temperature and humidity readings. This can affect how accurate the data is.
You should set up a weather station on flat, even ground. This helps stop water from building up and damaging the equipment. It also keeps the station stable and working well. This way, you can trust the weather data you collect.
Mounting the Weather Instruments:
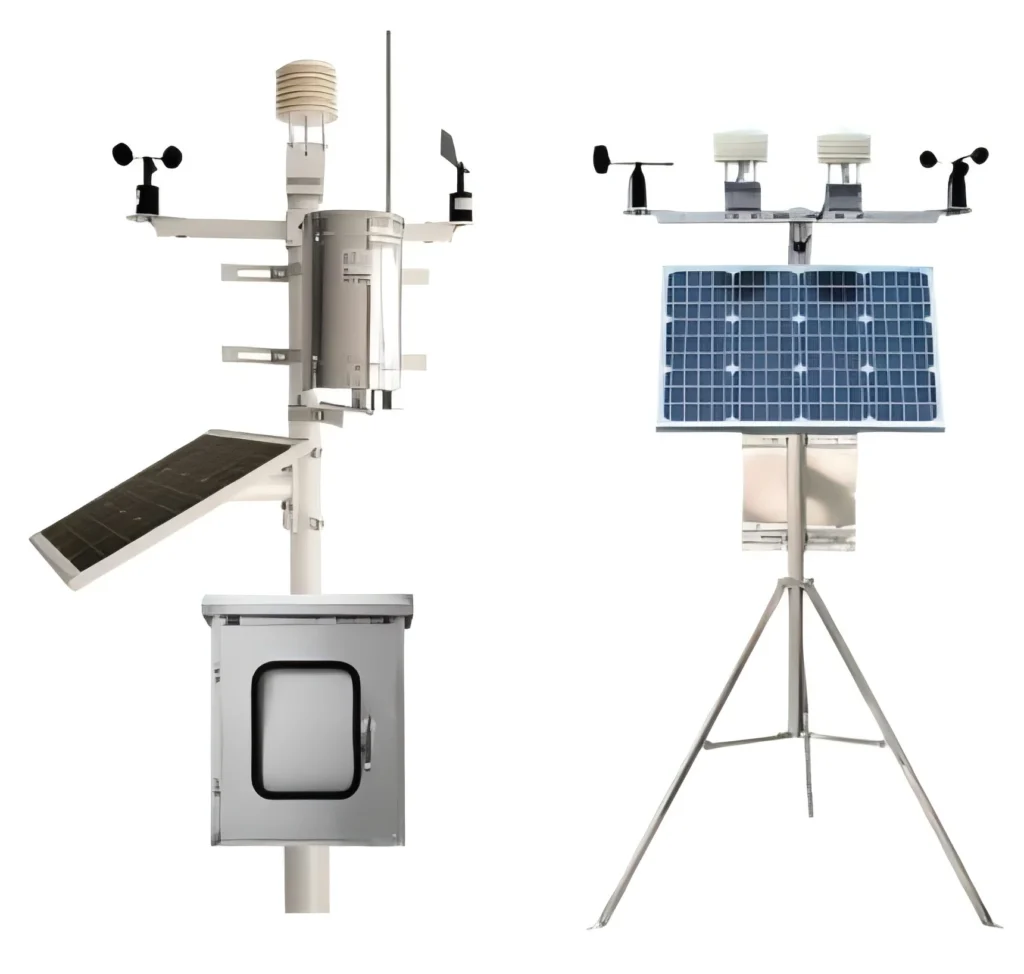
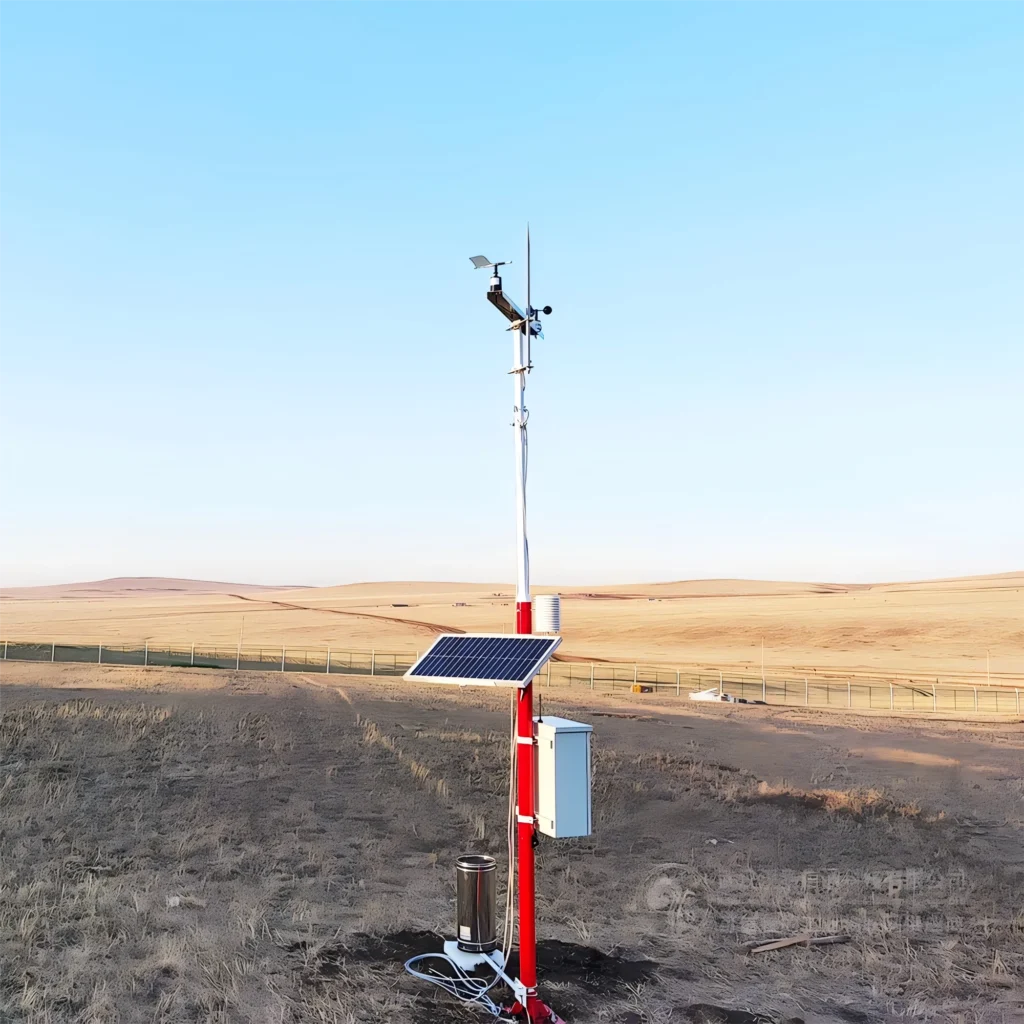
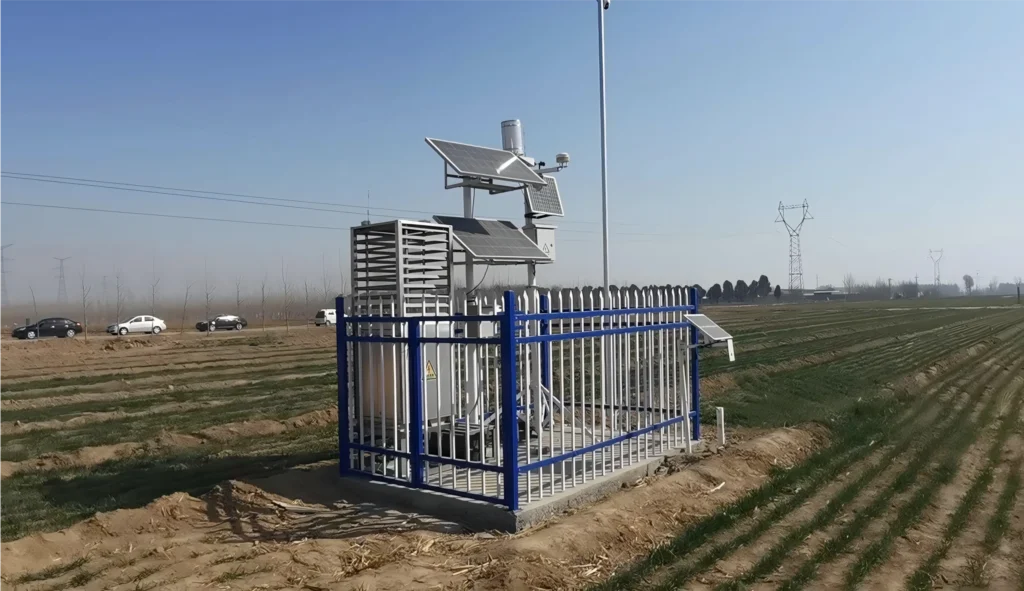
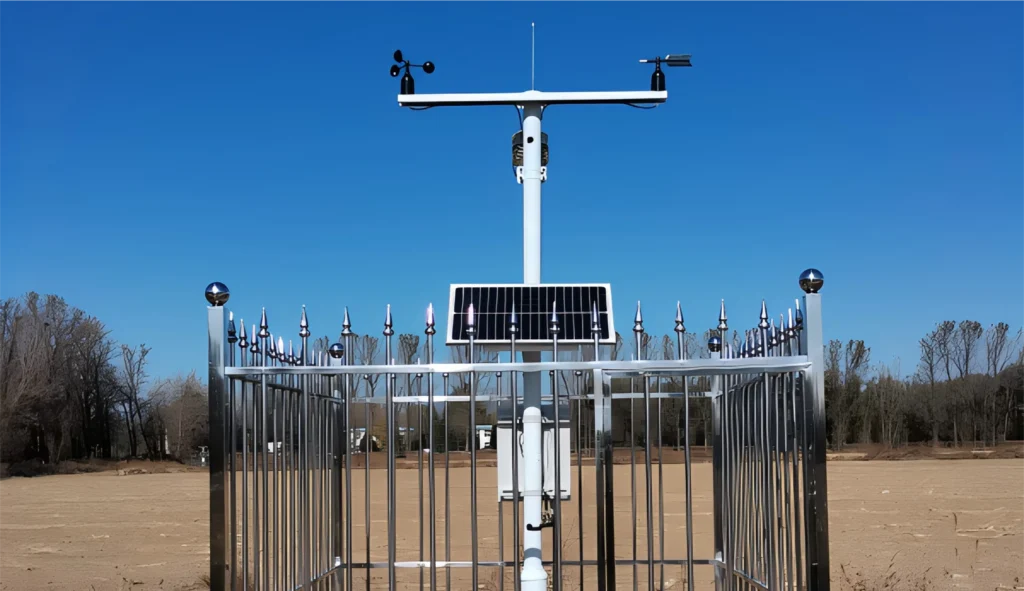
Place the anemometer, which measures wind speed and direction, on mounting poles. Make sure it is high above the ground. This times the height should let it sample wind flow without any obstacles. The best height to install anemometers is 10 meters, or 33 feet, above the ground.
Put the temperature and humidity sensors in a shaded spot. This will stop direct sunlight from changing the readings.
Power Supply:
Choose the power supply for your weather station. Some stations use batteries. Others need mains power or a solar panel to work all the real time.
Make sure the power source is reliable. Protect it from things like moisture and temperature changes.
Wiring and Connectivity:
For weather stations with wired sensors, like temperature or humidity sensors, planning is key. You must route the cables properly. The cables should be tightly secured and protected to avoid damage or problems.
You can use cable clips or tubes. These tools hold the wires in place. They also keep the wires safe from damage and protect the environment.
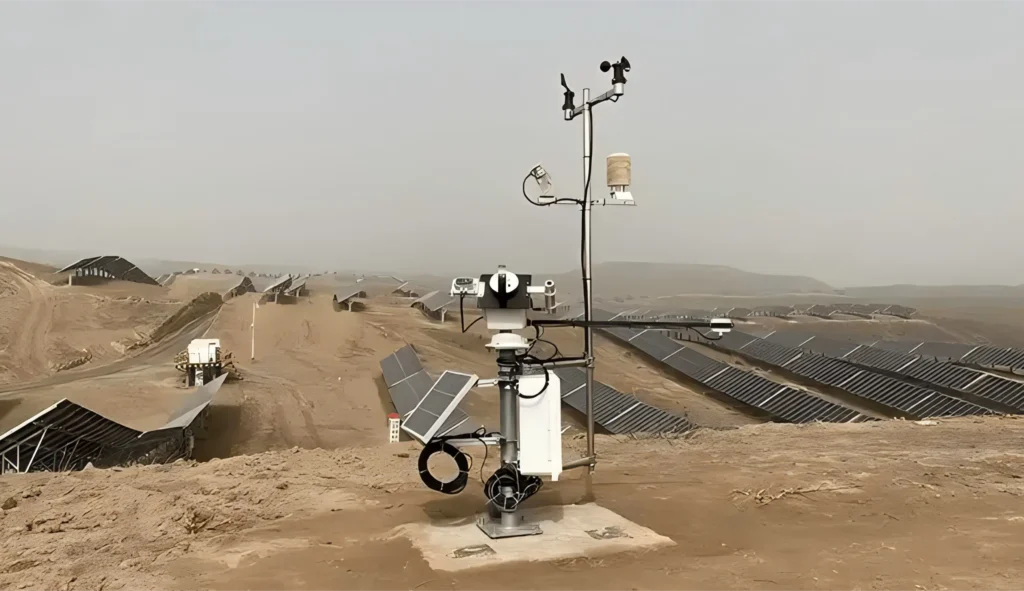
Photovoltaic industry weather station:
Lighting conditions:
The weather station needs a lot of light. It is important to keep away from tall buildings and trees. This helps us get precise weather readings of sunlight. Solar radiation data is key for checking how well solar power systems perform.
Representative area:
Pick a spot that reflects the weather of the area with the solar power station. If the station is large, place the weather station in the center. You can also put it close to the main power generation equipment.
Avoid interference sources:
Stay away from big heat sources, pollution sources, and sources of electromagnetic interference.
Photovoltaic panel Angle matching:
The radiation sensor should be placed on the same level as the solar panel. For fixed panels, the sensor needs to match the same angle.
The radiation sensor should be placed 1.5 to 2 meters above the ground. This height helps prevent problems like reflection and heat from the ground. It also makes daily maintenance and checks easier.
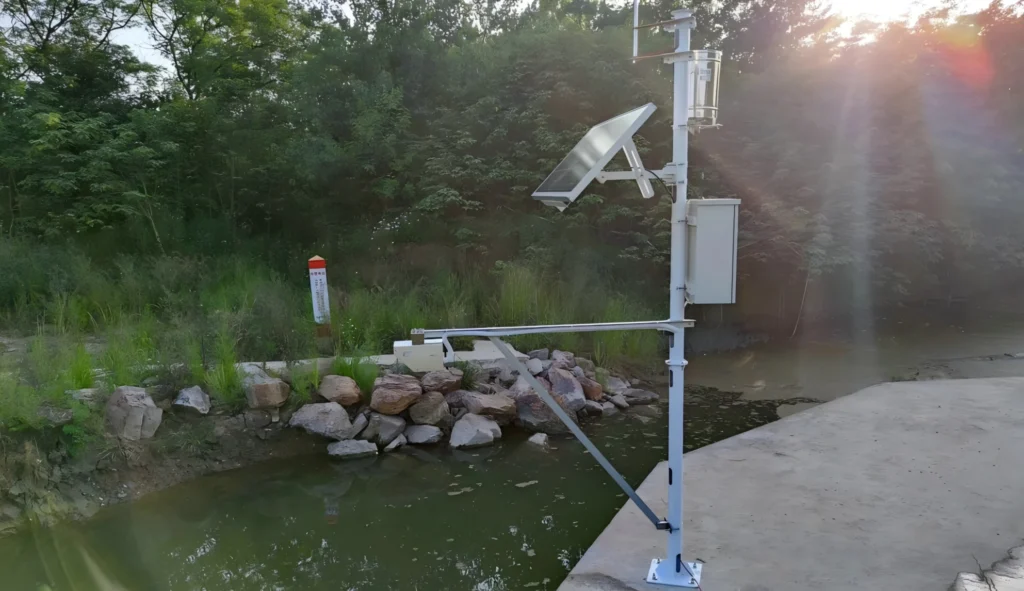
Hydrological monitoring weather station:
Close to water bodies:
You should set up a personal weather station near water. Place it by rivers, lakes, or reservoirs. This will help you get better data on water evaporation and rainfall.
Representativeness:
The weather conditions at the chosen site should reflect the whole monitoring area. When you look at a large reservoir, it is best to place the weather station on the central peninsula. You can also put it in an open area by the shore. This way, we can use the weather data we collect for water model calculations.
The weather station data shows temperature, humidity, wind speed, and wind direction.
These calculations apply to the whole reservoir area.
Waterproof and moisture-proof treatment:
Since there are water bodies nearby, the equipment needs to be waterproof and moisture-proof. All electrical devices and connection lines need to be waterproof.
Firmness and stability:
The weather station’s supports and instruments must be installed securely. The hydrologic monitoring area, especially near water, can have strong winds. It may also face severe weather, like heavy rain. The equipment should be set up with ways to protect it from the wind.
These measures can involve using a deep-buried foundation or a weighted base. This will help keep the equipment from falling over in strong winds.
smart agricultural ambient weather station installation:
Field representative area:
The weather station should be chosen to represent the weather conditions in the whole field area. For a large farm, it is best to place the station in the center of the field or near the main crop areas.
Avoid blocking and interference:
To measure solar radiation, rain, and wind accurately, stay away from tall buildings and trees. They can block the measurements.
Close to irrigation and drainage systems:
Being near irrigation water sources and drainage channels on farms makes it easy to check soil moisture. This helps us see how rain and irrigation impact the soil. This helps combine weather data with irrigation and drainage information better.
Installing height:
Temperature and humidity sensors are often placed 1.5 to 2 meters above the ground. This height is close to the crop canopy. It helps them better measure the temperature and humidity of the growing environment.
The rain sensor’s rain socket is usually 0.7 to 1 meter above the ground. This height stops splashing water from affecting the measurement.
environmental weather station:
Representative environmental areas:
We should set up weather stations in places that show the environment we monitor. To track the urban area, we can choose a mixed-use zone in the city. This zone should have homes, shops, and small factories. This way, we can collect full weather data that shows the urban area.
Away from sources of pollution and interference:
Avoid clear sources of pollution. These include places such as chemical plants and waste incinerators. Stay away from busy traffic areas, such as highways and railways. Lastly, keep away from large farms that use a lot of pesticides and fertilizers.
Geomorphic factors:
Pick flat and open places to set up weather stations. Do not place them in valleys or on steep slopes. Valleys can trap air and pollutants.
Install Height:
Install the general temperature and humidity sensor 1.5 to 2 meters above the ground. This helps reduce the effects of ground radiation and water vapor on the accurate readings. It also reflects the conditions where people typically work and live.
Install air quality sensors. Make sure their air intakes are 3 to 5 meters above the ground. This helps get accurate data on air pollution. It also stops dust and emissions from interfering near the ground.