Instrument used to measure wind speed & instrument to measure wind velocity & wind speed measuring device
Instruments that measure wind speed and wind direction are important in many fields. The anemometer is the most common tool for this. Anemometers come in different types, such as wind cup anemometers, wind vanes, and laser Doppler wind radars.
Anemometers can work alone or as part of a bigger system for weather observation and forecasting. They are also used to protect the environment, save energy, and in aerospace, among other things.
The main types of anemometers include:
1. **Wind Cup Anemometer**
This is a tool that measures how fast the wind blows. It has three or four cup-shaped parts on its arms. These moving parts that move are flat. When the wind blows, the cups turn.
Their spinning speed is linked to the understand accurate wind speed. We can find the precise wind speed by measuring how fast it spins.
2. **Wind Vane**
A wind vane shows which way the wind is blowing. It usually has a pole and a rotating arrow or blade that points with the wind.
3. **Wind Rod**
A wind rod is a tool that has both a wind vane and an anemometer. It measures both wind direction and speed in one device.
4. **Laser Doppler Wind Radar**
This advanced device uses laser technology to measure wind direction and speed without contact. Its non-contact method avoids issues like friction and vibrations. This ensures high accuracy and sensitivity. However, it has high costs and needs skilled operation and maintenance.
5. **Ultrasonic Anemometer**
This type uses sound waves that are too high for humans to hear. Ultrasonic sound waves anemometer determine wind speed how fast the wind blows and which way it is going. It provides strong and accurate results in a small design.
6. **Hot-Wire Anemometer**
This wind speed measuring device has a thin wire. It heats up when electricity flows through it. It speeds measured airflow by checking how fast heat leaves the wire into the moving air.
Each type of anemometer has its own features and accuracy levels. They are helpful in many situations. Choosing the right instrument for wind speed depends on what you need it for and the situation. This choice helps ensure the best performance.
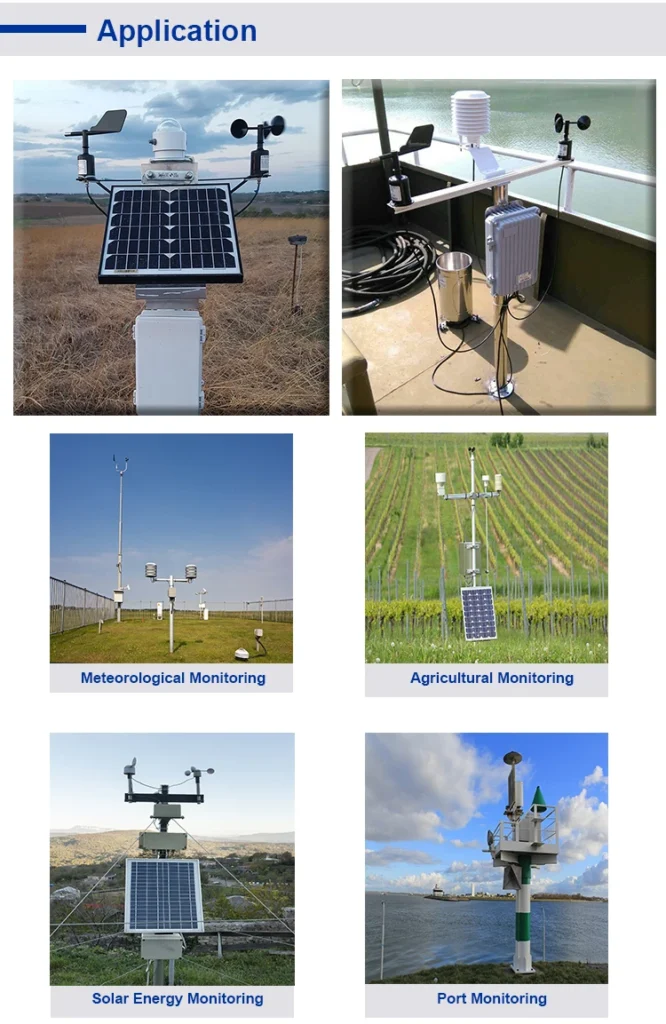
Applications of Anemometers
1. **Wind Energy Resource Assessment**
Anemometers measure key factors such as average wind speed, direction, temperature, humidity, air pressure, and sunlight. This data helps assess the potential of wind farms. By looking at wind conditions at various heights, they give key information for creating and improving wind energy projects.
2. **Aviation**
Measuring instrument airspeed and airflow direction is important for designing and testing planes. Anemometers measure how strong the wind is. They help make designs stronger and more stable.
And they also make sure flights are safe. They also help improve how well aircraft, rockets, and other aerospace vehicles perform.
3. **Energy Sector**
In solar energy, anemometers help find the best spot and angle for mirrors or solar panels. This boosts energy capture in solar power plants.
4. **Meteorological Observation**
Weather forecasting uses data from calculate wind speed meters. This helps us look at wind weather patterns, predict storms, and study climate trends.
5. **Environmental Monitoring**
Anemometers measure how air pollutants spread and move. They help us learn about pollution levels in the environment. This information helps create and carry out environmental policies.
Anemometers are helpful tools that solve problems in many fields. They can work by themselves or in groups. They provide accurate data that helps with research, technology, and managing resources in a sustainable way.
Maintaining anemometer
It is important to keep your anemometer in good shape. This helps it stay accurate and last longer. Here are some steps to keep your device in good shape:
Clean the anemometer often. Make sure to pay close attention to the wind gauge sensor. This helps keep dust, dirt, and debris from affecting accuracy. Disinfect when needed for extra protection.
Periodic calibration: To keep your anemometer accurate, calibrate it often. You can have professional technicians do this, or you can use standard equipment to calibrate it yourself.
Avoid corrosive substances. Keep the sensor away from acids and bases. These can harm its delicate parts.
Keep the device away from strong vibrations and hard hits. This will help reduce exposure to vibrations. This keeps it accurate and protects its inner parts.
Store in a dry place: Keep the anemometer in a dry spot. This will help keep it safe from moisture.
Fix problems quickly: If you see any issues or breakdowns, do maintenance or repairs right away. This helps avoid long breaks and keeps the device running smoothly.
By using these tips, you can make your anemometer last longer. This will help it provide accurate measurements each time.
The anemometer is a key tool used in many industries. Its data helps make wind energy better. It also helps with aerospace, protects the environment, and studies climate change.
Taking care of it helps it provide reliable information. This information drives progress in these areas.