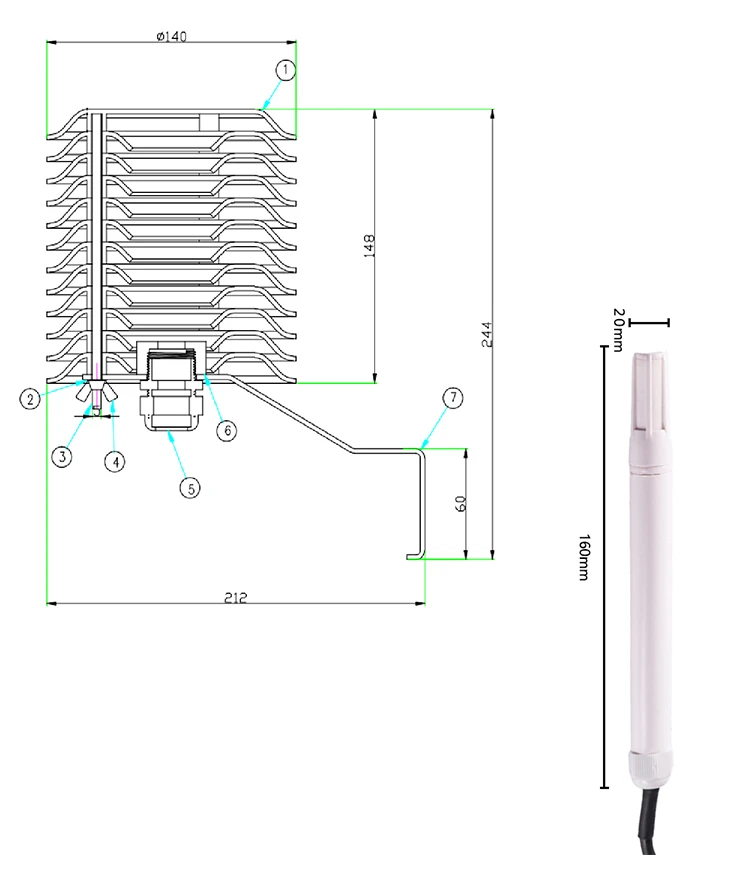
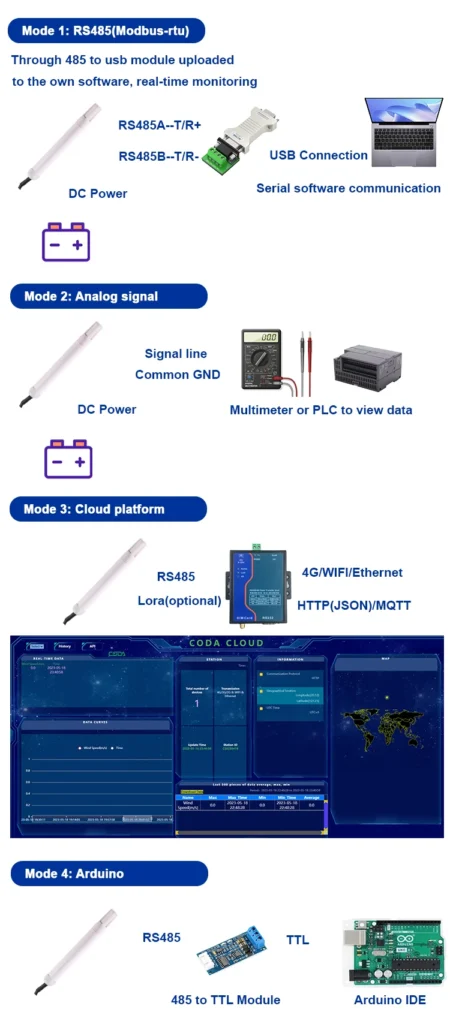
How Do Humidity Sensors Work
In our connected world, it is important to keep the right environmental conditions. This affects many parts of our lives, from industry to comfort at home. Humidity sensors play a key role in this process.
They quietly and effectively check the moisture in the ambient air. But how do these humidity sensors function?
The Basics of Humidity Measurement
Humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air. There are different ways to measure humidity. Relative humidity (RH) is the most common way to express it.
Relative humidity shows how much absorbs water vapor is in the air. It compares this amount to the most the air can hold at a certain temperature. We show this as a percentage. Manufacturers make humidity sensors to find and measure water vapor.
These sensors change the vapor into an electrical signal. This signal is easy to measure absolute humidity and understand.
types of humidity sensors and Their Working Principles
Capacitive Humidity Sensors
Capacitive humidity sensors are one of the most common types used. They operate based on the principle of capacitance change.
The sensor has two conductive plates. A material that responds to humidity is placed between these plates. This material is often a polymer or a metal-oxide film.
When the air has water vapor, this material takes in moisture on its surface. As water molecules build up, the material’s dielectric constant changes. Since the dielectric constant affects capacitance, this change impacts the sensor’s capacitance.
The sensor measures the amount changes in capacitance. This change relates to the humidity level. It can accurately find the air’s relative humidity.
Capacitive sensors have many benefits. They respond quickly, are very accurate, and have good long-term stability.
They are great for many uses. This includes weather stations that need quick and accurate humidity readings. They also work well in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems for homes and offices.
Resistive Humidity Sensors
Resistive humidity sensors work by using the change in resistance of the electrodes a sensing element when humidity changes. Manufacturers often use a material that soaks up moisture for the sensing part. This can be either salt or a conductive polymer.
Hygroscopic materials can pull in and hold water vapor from the air. When humidity goes up, the sensing element takes in more water vapor.
This change affects how well it carries electricity and how much it resists. When the sensor’s resistance changes, a circuit can measure it. The system gets the sensor ready to connect resistance values with humidity levels.
This lets it change the measured resistance into a precise humidity reading. Resistive sensors are simple and cost-effective. This makes them a popular choice for home humidity monitors.
In these cases, cost and basic features matter. Farmers use them to check soil and air moisture. This helps farmers water their crops and grow them better.
Thermal Conductivity Humidity Sensors
Thermal conductivity humidity sensors work because water vapor affects how well air conducts heat. These sensors have a heated part that checks the air temperature. When air with different humidity levels passes over the heated part, the rate of heat transfer changes.
Water vapor carries heat differently than dry air. When humidity goes up, the air’s heat conduction changes. This affects how quickly the heated element loses heat.
The sensor measures changes in heat transfer. This change connects to the humidity level. By doing this, the sensor can find the relative humidity. Thermal conductivity sensors are very reliable in industrial settings.
They can work well in tough conditions and are less affected by dirt than other sensor types. People often use them to make semiconductors. Controlling humidity is important for the quality of electronic parts. Some chemical processing tasks also use these sensors.
Optical Humidity Sensors
Optical humidity sensors work by using the interaction between light and materials that respond to humidity. One method uses materials that change their look when they come into contact with water vapor. These changes can include color shifts or changes in how light bends. Some dyes or polymers change color when they absorb moisture.
The refractive index of a material can change with humidity. The sensor uses light-emitting and light-detecting parts to measure these changes. Another type of optical humidity sensor detects light scattering.
This occurs when water droplets or particles are in the air. The humidity level relates to the light scattered. This helps the sensor calculate the relative humidity. Optical sensors are very sensitive and can give detailed measurements.
They are also safe from electromagnetic interference. This makes them useful in places where electrical noise can disrupt other sensors. Optical humidity sensors are used in science. They measure how much moisture is in living things.
They are also used in some industries. These sensors give precise and non-invasive humidity readings.
The Role of Signal Processing
Once a humidity sensor detects a change, it turns this change into an electrical signal. This signal often needs more work. Engineers use signal conditioning circuits to make electrical signals stronger and clearer. This helps improve their quality.
This makes the signal better and more accurate. Then, the system sends the processed signal to a microcontroller or a data acquisition system.
These devices can do more calculations and make more adjustments. They can also convert the signal into an easy-to-use format.
For example, they can show the humidity level on a digital screen. They can also give an analog output. This output can control other devices, like humidifiers or dehumidifiers, in an automated system.
Applications of Humidity Sensors
Humidity sensors are very helpful and are used in many industries. In medicine, it is important to keep the right humidity levels in hospitals and labs.
In operating rooms, humidity sensors help keep the air just right. If the air is too dry, it can create static electricity. This can harm sensitive medical equipment.
If the air is too humid, it can help bacteria and fungi grow. In the food and drink industry, companies use humidity sensors to check storage conditions. Good humidity control helps stop spoilage and keeps the texture and flavor of food.
It also makes products last longer. In the car industry, humidity sensors are used in climate control systems. This helps keep passengers comfortable and healthy.
In conclusion
Humidity sensors are special tools that measure how much moisture is in the air. They use various ways to do this. These sensors change humidity levels into electrical signals.
They process these signals. This makes them helpful tools for many uses.
As technology improves, we can expect better humidity sensors. These sensors will be more accurate, reliable, and smart. They will help us monitor and control our environment even more effectively.