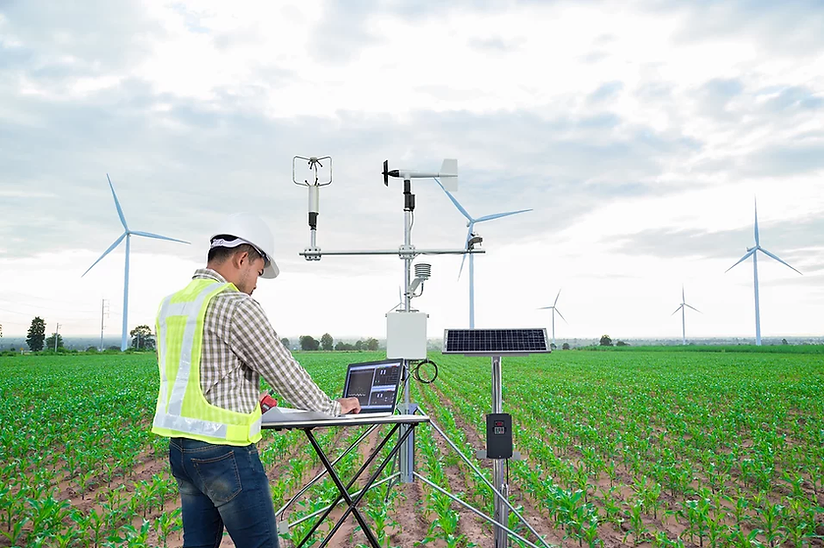
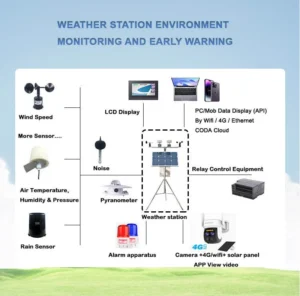
Environmental Meteorological Monitoring Instruments
Environmental meteorological monitoring instruments are essential for measuring a range of environmental and meteorological parameters. Below are some of the most common types:
Temperature and Humidity Monitoring Instruments
Thermometer:
Used to measure ambient air temperature, thermometers come in various types including mercury, alcohol, and electronic thermometers. In contemporary environmental monitoring, electronic thermometers are preferred due to their precision and quick response times.
Hygrometer:
This instrument determines air humidity levels. Common variants include mechanical, electronic, and dew-point hygrometers. Electronic hygrometers are favored for their ease of use and reliable measurements of relative humidity.
Pressure Monitoring Instruments
Barometer:
Designed to measure atmospheric pressure, traditional barometers include mercury and aneroid types. Modern digital barometers, however, are increasingly popular thanks to their accuracy and seamless integration with meteorological systems.
Wind Monitoring Instruments
Anemometer:
An anemometer gauges wind speed. Older models include cup and propeller designs, while more advanced tools like ultrasonic and laser-Doppler anemometers offer contactless measurement with high accuracy.
Wind Vane:
This instrument determines wind direction with a simple mechanical pointer that aligns with the wind. Advanced versions incorporate electronic sensors for more precise and detailed wind-direction data.
Precipitation Monitoring Instruments
Rain Gauge:
Measures rainfall by collecting water in a container, where the depth indicates the amount of precipitation. More sophisticated models, such as tipping-bucket and weighing rain gauges, can automatically log and transmit rainfall data.
Snow Gauge:
Used to quantify snowfall, snow gauges come in different forms. A common example is the weighing-type snow gauge, which determines snowfall by measuring the weight of accumulated snow.
Radiation Monitoring Instruments
Pyranometer:
Captures global solar radiation, including both direct and diffuse light. It is widely used in meteorology and solar energy applications to evaluate solar energy availability.
Pyrheliometer:
Measures direct normal solar radiation by assessing sunlight intensity in a specific direction. This is crucial for designing solar power plants and evaluating solar energy resources.
Air Quality Monitoring Instruments
Particulate Matter (PM) Monitor:
Tracks airborne particulate matter concentrations, including PM10 and PM2.5. Measurement techniques vary and include optical scattering, beta-ray attenuation, and tapered element oscillating microbalance (TEOM).
Gas Analyzers:
Measure concentrations of gases such as sulfur dioxide (SO₂), nitrogen oxides (NOₓ), carbon monoxide (CO), and ozone (O₃). Detection methods differ and range from electrochemical sensors to infrared absorption and ultraviolet fluorescence techniques.