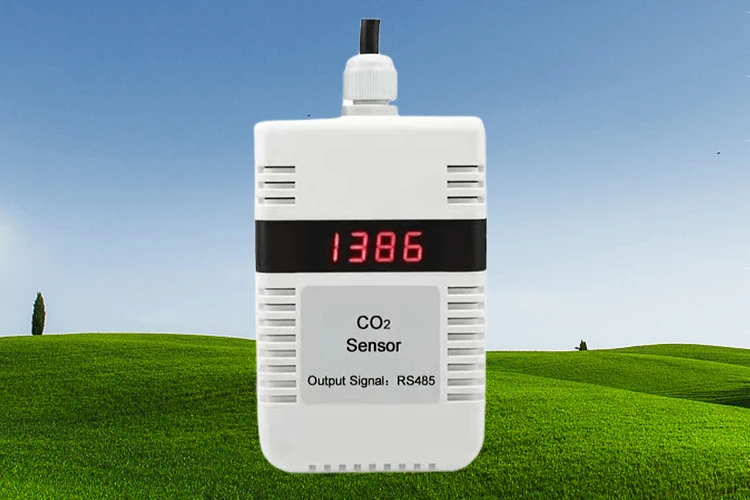
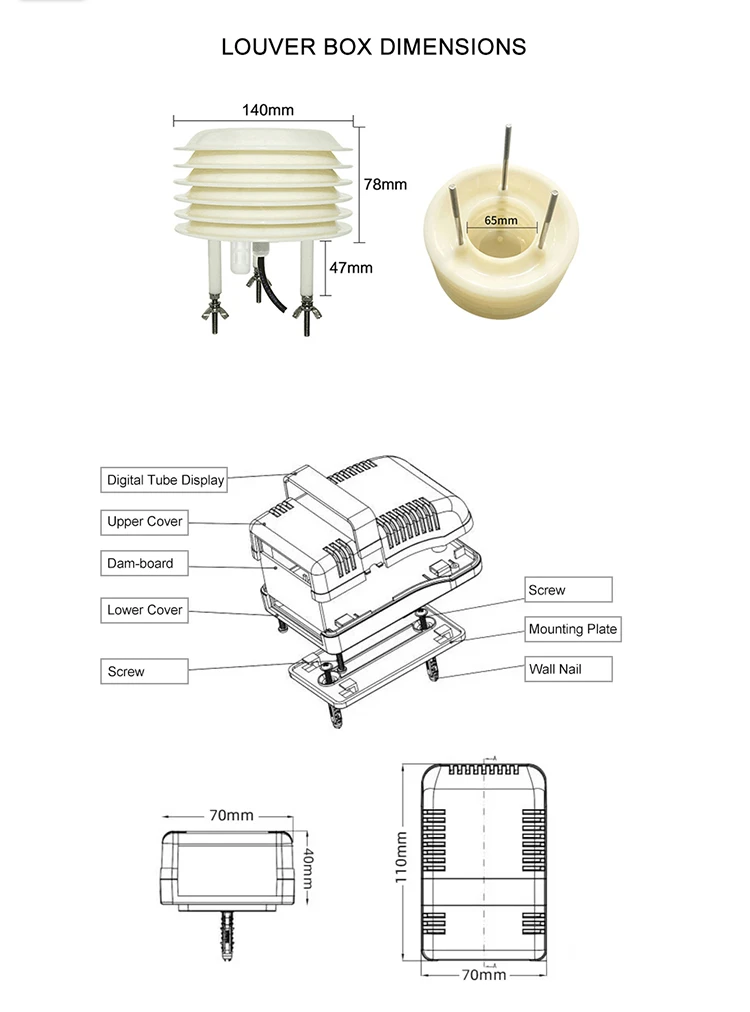
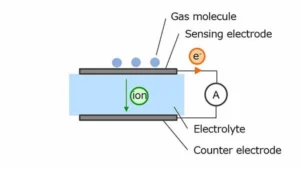
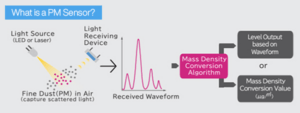
what is a pm2 5 sensor
In recent years, air quality has become a growing concern around the world. pm2.5 refers is fine dust that is 2.5 micrometers wide or smaller.
It is important because it can harm human health. Pm 2.5 sensors are helpful tools for finding and tracking this pollutant. Many areas use these sensors.
1. Environmental Monitoring
1.1 Urban Air Quality Surveillance
In cities, PM2.5 sensors are found in many places. These include downtown, industrial areas, and neighborhoods. These sensors measure PM2.5 levels in the air all the time. Researchers combine and study data from different sensors to show a clear view of the city’s air quality.
In big cities like Beijing and Delhi, officials have set up a network of PM2.5 sensors. The real-time data helps local environmental agencies quickly find areas with high pollution levels.
You can use this information to make specific pollution control measures. This could mean reducing vehicle emissions in some areas. It may also mean stopping industrial work in polluted areas for a short time.
1.2 Industrial Pollution Monitoring
Industries are major sources of PM2.5 emissions. Factories that make coal power, steel, and cement need to install PM2.5 sensors. This is required by regulators. These sensors check the emissions from factories.
Industries can check PM2.5 levels in vehicle exhaust gases to follow environmental rules. If the sensors show high emissions, they can act fast.
They can upgrade their pollution control tools or improve how they make products. This helps protect the environment. It also avoids fines and legal issues for not following the rules.
2. Health – related Applications
2.1 Healthcare Facilities
Hospitals and clinics are using PM2.5 tiny particles sensors more often. These sensors help keep the indoor air clean and healthy. Patients with breathing issues are more affected by air pollution. So, it is important to monitor the air quality in these places.
PM2.5 sensors in waiting rooms, patient wards, and operating rooms can find changes in air quality. When 2.5 microns levels are too high, open windows for fresh air or use air purifiers. This helps lower the risk of exposing patients to harmful particles. These particles can make their health problems worse.
2.2 Personal Health Monitoring
With the rise of wearable technology, personal PM2.5 sensors have become available. You can attach these small sensors to your clothes or carry them in your pocket. They keep track of PM2.5 levels around you all the time.
For people with breathing problems like asthma or COPD, these sensors give real-time air quality information. By using the readings, they can change outdoor activities or take steps to stay safe.
For example, they can wear masks when PM2.5 levels are high. People who care about fitness and air quality can use these sensors. They can choose to work out in places with cleaner air.
3. Smart Home and Indoor Air Quality Management
3.1 Automated Air Purification Systems
In smart homes, PM2.5 sensors are part of automated air purifiers. These sensors check indoor PM2.5 levels all the time. When PM2.5 levels rise above a certain limit, the air purifier turns on.
The air purifier begins to clean the air. As PM2.5 levels go down, it can change its fan speed or turn off. This keeps the indoor air healthy and saves energy. For example, in a home near a busy road, the PM2.5 sensor can sense when dust and pollutants from traffic enter the house.
3.2 Ventilation Control
PM2.5 sensors can also be used to control the ventilation systems in homes. When outdoor air quality is good, sensors find low PM2.5 levels. They then tell the ventilation system to open the windows or let in more fresh air.
When outdoor PM2.5 levels are high, we can change the ventilation system. This lowers the amount of polluted air coming in and recirculates the air inside. This smart control of ventilation helps balance indoor air quality and energy use.
4. Transportation and Traffic Managemen
4.1 Vehicle Emission Monitoring
In transportation, PM2.5 sensors are used to check vehicle emissions. Some car makers add these sensors to new vehicles. These sensors measure the PM2.5 that comes from the vehicle’s engine.
For diesel vehicles, particulate matter sensor play a key role. They help keep track of PM2.5 emissions. If a sensor finds high emissions, it can alert the driver. The driver might need to take the car for maintenance.
This could mean replacing a clogged air filter or tuning the engine. In some cities, officials use sensors to measure PM2.5 levels by the road. These sensors help check air quality in busy traffic areas.
4.2 Aviation and Airport Air Quality
Airports are now using PM2.5 sensors. These sensors check the particles in the air quality inside and around the airport. Aircraft engines release small particles when they take off, land, and taxi. They place PM2.5 sensors near runways and in terminals.
They can measure how these emissions impact local air quality. We use this information to make plans that reduce the environmental impact of airport operations. Airports can promote the use of alternative fuels for planes. They can also improve ground-handling methods to cut down emissions.
In conclusion, pm2.5 particles sensors play a key role in many areas of our lives. They have many uses. They help protect the environment.
Also can improve personal health. They manage smart homes and support transportation.
As technology gets better, these sensors will likely be more accurate and cheaper. They will also work better with different systems. This will help make a cleaner and healthier environment.