best smart sensors for farming
Why greenhouses should incorporate sensors
The main goal of adding best sensors for greenhouse monitoring and manage the environment inside. This helps improve the quality and yield of crops. Here are several key reasons best smart sensors for sustainable farming practices :
Real-Time Monitoring
Sensors provide real-time data driven decisions. This helps farmers quickly change greenhouse conditions. As a result, crops receive what they need at each growth stage.
Better Environmental Control
Agricultural sensors help control temperature, humidity, light, and CO₂ levels. This creates the best conditions for plants to grow.
Less Manual Work
Sensors can monitor and adjust soil conditions automatically. This cuts down on labor, lowers costs, and improves efficiency and crop health quality.
Pest and Disease Prevention
Poor greenhouse conditions can cause pests and diseases. Sensors provide early warnings so farmers can act fast and reduce losses.
8 Types Of Sensors For Optimal Greenhouse Performance
Greenhouses often employ a range of sensors to oversee and manage environmental conditions, with common types including:
1.Temperature sensors:
These devices track greenhouse temperature changes in the greenhouse. They help control heating and ventilation systems. This keeps the temperature just right for plant health growth.
Temperature sensors provide real-time data on the greenhouse’s temperature. This helps adjust heating and ventilation. Keeping crops in the right temperature range improves both yield and quality.
2.Humidity sensors:
These devices measure the air’s humidity levels. They help manage irrigation systems and ventilation equipment. This keeps humidity at the right level.
Humidity sensors provide real-time data on moisture levels. This helps farmers adjust irrigation and ventilation to keep ideal humidity. Proper humidity helps plants absorb water, grow well, and avoid pests and diseases.
3.Light Sensor:
These sensors track light intensity. They help adjust shade cloths or extra lighting. This ensures crops get the right amount of light.
Light sensors give real-time data on light levels. This helps farmers use shading or lighting to make sure crops get the right amount of light. Light is key for energy production and healthy plant growth.
Farmers can use light sensor to take advantage of natural light. They can also add extra lighting when needed to improve crop growth.
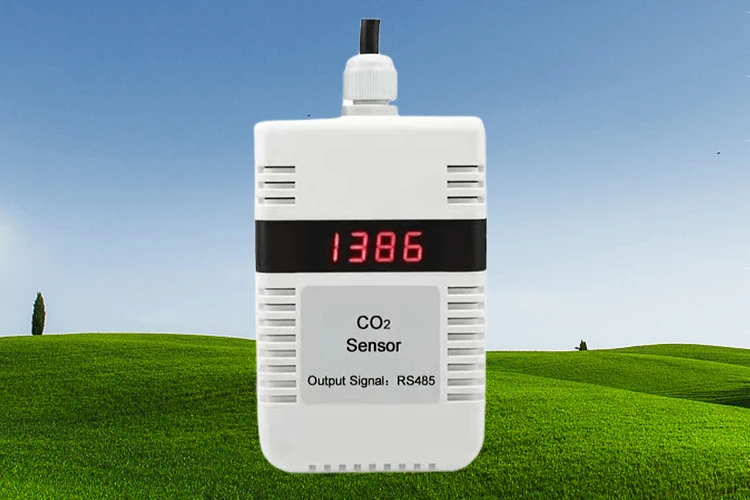
4. CO2 Sensor:
This device measures the carbon dioxide levels in the greenhouse. It helps improve airflow and CO2 supply for better plant energy production.
CO2 sensors give real-time data on CO2 levels. This helps farmers manage ventilation and carbon dioxide supply. As a result, plants can turn light into energy and grow better.
Keeping the right CO2 levels helps plants use light for energy. It also helps them absorb nutrients and grow stronger. CO2 sensors help farmers control greenhouse weather conditions. This improves crop yield and quality.
5. Soil Moisture Sensor:
These sensors go into the soil to measure moisture levels. They help control irrigation systems, so there is not too much or too little water.
Soil moisture sensors provide accurate information about monitoring soil. This helps farmers manage irrigation schedules systems better. They can avoid over-saturation or excessive dryness. By adjusting irrigation levels on time, farmers keep soil moisture temperature at the right level. This ensures plants get enough water and reduces waste. It also helps prevent root diseases.
The main job of these sensors is to give accurate, real-time data. This data helps farmers manage greenhouse conditions better. It improves the growing conditions environment and increases crop yield and quality.
6.Soil nutrient sensors
Make sure to fertilize correctly, avoid nutrient shortages, and cut down pollution from runoff. Some soil nutrient sensors use chemical methods to check nutrient levels.
For example, electrodes in the sensor react with certain ions in the soil like nitrogen, phosphorus, or potassium. The sensor measures the electrical current or voltage, which shows the nutrient level.
This data helps farmers use the right amount of fertilizer, saving money and preventing pollution from too much runoff.
7.pH sensors
Keep the right pH for crops to make sure they get enough nutrients. Soil pH sensors often use a glass electrode. This electrode reacts to hydrogen ions in the soil. When the sensor is placed in soil, it creates a voltage. This voltage shows how many hydrogen ions are present.
The sensor changes voltage into a pH value. Different crops grow best in different pH levels. – Blueberries prefer acidic soil. Their ideal pH is between 4 and 5.
– Broccoli grows best in slightly acidic to neutral soil. This means a pH of 6 to 7 is ideal for them.
– Farmers can use pH sensors to check and adjust the soil pH. They use lime to raise pH or sulfur to lower it, meeting crop needs.
8.Water quality sensors
Water quality sensors help keep irrigation safe and effective. They measure things like pH, dissolved oxygen, turbidity, and harmful chemicals. For example, a pH sensor checks if the irrigation water has the right pH for crops. If the water is too acidic or too alkaline, it can hurt nutrient absorption and damage plant roots.
Dissolved oxygen sensors are important in hydroponics and for crops with sensitive roots. Low oxygen levels can lead to root rot. Turbidity sensors measure water clarity. High turbidity means more particles in the water, which can block irrigation systems or hurt plant growth.
When using greenhouse sensors, you should think about several important environmental factors:
1.Select the appropriate sensor:
Different greenhouse sensors have different purposes and uses. When picking a sensor, make sure it fits your needs and greenhouse type. Check that the sensor provides the data you need and works with your other equipment or systems.
2. Location and method of installation:
The placement of the sensor is very important for accurate data collection. Choose a good spot for installation. This will help avoid problems from direct sunlight, strong winds, or other disruptions.
Also, make sure there is enough space between the sensor and nearby plants or objects. This will prevent errors or interference.
3. Calibration and Maintenance:
To keep the sensor accurate, you need to calibrate and maintain it regularly. Follow the sensor’s guidelines for checks and calibrations. This helps it work properly and provide accurate data.
4. Data Interpretation and Decision-Making:
Accurate sensor data is important, but making smart decisions is even more crucial. Acting based on this data is key.
After you collect sensor data, you need to analyze it carefully. Then, you should make decisions based on your findings. This process needs some special knowledge and experience. However, you can use greenhouse management software or get expert advice.
Benefits of using smart sensors in modern agriculture
Increased Yields: Accurate data from soil, weather, and optimal crop sensors help farmers make better choices. This leads to healthier plants and bigger harvests. For example, soil moisture sensors make sure plants get the right amount of water. This helps avoid drought stress and overwatering.
Resource Optimization: Smart sensors help save water, fertilizers, and energy. Soil nutrient sensors allow farmers to use only what they need. This cuts waste and lowers costs. Weather sensors help manage greenhouse heating and cooling based on real conditions.
Reduced Environmental Impact: Using enable precise fertilization lowers chemical runoff. This helps protect water and soil. Sensors match fertilizer to the soil’s needs, which reduces pollution.
Cost Effectiveness: Using resources only when needed lowers costs. Early detection of pests and diseases with sensors allows for targeted treatments. This reduces pesticide use and saves money.
Improved Decision-Making: Real-time sensor data helps farmers make quick and accurate choices. They know when to irrigate, apply pesticides, or change greenhouse settings. This is better than relying on guesswork.
The future of smart sensors in agriculture
As technology keeps improving, smart sensors in precision agriculture have a bright future. Here are some trends to watch for:
Smart sensors will work better with other farm tools like tractors, drones, and irrigation systems. For example, drones can collect data and tell tractors where to apply fertilizers or pesticides.
Advanced Analytics: Strong data tools and machine learning will look at sensor data. This helps predict weather patterns, crop diseases, and pests. Farmers can act early to protect their crops.
Miniaturization and Cost Reduction: Sensors will become smaller and cheaper. This means more farmers, including small ones, can afford smart farming sensor technology.
Sustainable Energy Solutions: Sensors will use green energy sources such as solar power or kinetic energy. This makes them eco-friendly and less reliant on regular electricity.
In summary
To use the best smart sensors for greenhouse precision farming, you need to pick the right one. You also have to install and take care of it properly.
Next, interpret the data correctly and make wise choices. It is also important to focus on data security and privacy. This method will improve the sensor’s performance and boost the efficiency of greenhouse management.