what does orp stand for
An ORP sensor checks the redox state of a solution. ORP stands for oxidation reduction potential orp. Here is a clear introduction:
how does an orp sensor work?
Basic Principle
It is based on redox reactions. In a solution, reductants such as nitrites and sulfides can turn into oxidize or reduce substances.
These include nitrates and sulfates. This process moves electrons. The ORP sensor checks the redox state of the solution. It does this by measuring how many electrons are moved.
Structure
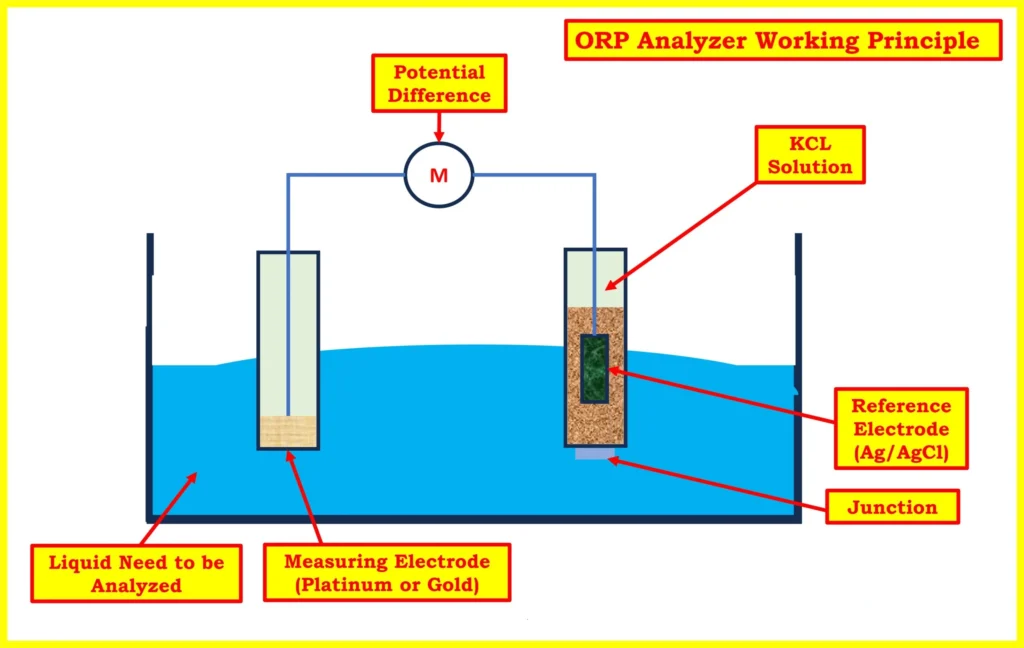
Electrodes usually have two parts: a reference electrode and a measuring electrode. The reference electrode is often made of Ag/AgCl in a KCl solution.
It produces a steady voltage of about 220 millivolts mv. It has a porous liquid junction that lets the electrolyte mix with the liquid. Manufacturers often use platinum or gold for the measuring electrode. These materials are stable and have good electrochemical activity.
Connection Circuitry: Made up of electronic parts like amplifiers, filters, and converters. It takes the signal from the electrode and turns it into a measurable electrical output. It also connects to send measurements to a data acquisition system or control system.
Measurement Process
Signal Detection: When the sensor is in the solution, the measuring electrode detects the redox reaction. It then creates a change in potential.
Signal Amplification: The change is often small. You need an amplifier to make the signal easy to measured in millivolts.
Signal Processing: The amplified signal can have noise or interference. People use filters to clean and improve the signal. This helps make sure the output signal is stable and accurate.
Signal Conversion: The system changes the processed signal into digital or analog form. This often happens with an analog-to-digital converter, known as an ADC. The output then goes to a data acquisition system or a control system.
Applications
Water Quality Monitoring:
It can measure the redox state of water accurately. This helps us learn about water chemistry and the environment. Researchers use it to find pollutants in wastewater treatment. This includes heavy metals, ions, chlorides, and nitrites that are found in water.
Industrial Applications:
In chemical production, it checks the redox status of the reaction. This helps keep the process stable and the product quality high. In metal processing, it can check the surface of the metal for oxidation. It can also check for problems like rust and color changes.
Environmental monitoring:
Sensors help scientists track the redox state of the air. Researchers also use them to check soil and drinking water. This helps assess environmental pollution.
Research laboratories:
It use it for the mechanism research and process control of various chemical reactions.
Advantages
High Accuracy: It can accurately measure the redox potential of the solution.
Good Stability: It can provide stable and reliable measurement results in different environments.
Wide Application Range: It is used in many areas. These tasks include checking water quality, watching industrial production, and observing the environment.
Limitations
Interference: Things like temperature, ph sensors measurement, and other substances in the solution can change the measurement results.
Calibration Requirement: You need to calibrate it often to get accurate measurement results.
How to calibrate ORP sensors?
Preparation
Check the Sensor: Make sure the high orp electrodes is working well. The probe should be undamaged, and the connections should be secure.
Prepare Calibration Solutions: Get at least two calibration solutions with known orp levels values. Common points are 220 mV for strong oxidizing and 470 mV for reducing agents. Make sure the solutions are fresh and clean.
Gather Tools: Get a clean beaker or container for the calibration solutions. You will also need a stirring rod to mix them. Use distilled water to rinse the probe.
Calibration Process
Clean the Probe: Rinse the ORP probe with distilled water. This will remove any leftover substances from past readings. If the probe was in another solution, let it sit in the air for a moment.
Two-Point Calibration
Calibration of the Oxidizing Solution: Place the probe in the oxidizing calibration solution, such as 220 mV. Stir gently for even contact. Wait for the ORP measurement to stabilize.
This may take a few minutes.
Next, adjust the ORP meter. Use the calibration controls to set it to the known value of the solution.
To make the solution, first rinse the probe with distilled water. This gets rid of any leftover oxidizing solution. Next, place the probe in the reducing calibration solution, such as 470 mV, and stir gently.
Wait for the orp reading to calm down. Next, change the meter to match the known value of the solution.
You can use various calibration solutions that have different ORP values. This will help make things more precise.
Place the probe in each solution. Wait for it to stabilize. Adjust the meter to get accurate readings across the full range.
Verification and Recording
Check the Calibration: Dip the probe in both calibration solutions again. This checks if the calibration is correct. Make sure the meter shows the right readings. Adjust the calibration if needed for accurate measurements.
Record Information: Write down the calibration data. Please include the values of the calibration solutions that were used. “Write down the time of calibration and any settings you adjust.” This is important for keeping track in the future.
Post-Calibration Maintenance
Clean the Probe: After you calibrate, rinse the probe with distilled water.
Regular Calibration: Calibrate the ORP sensor often. Use this based on how much you use it and where you are. This keeps it accurate and reliable.