Understanding Soil NPK: Helping Your Plants Thrive
Soil nutrients are essential for plants to grow. Just like humans need a balanced diet of meat and protein, plants need nutrients from the soil to grow. Nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) are key elements for healthy plant growth.
Plants use these nutrients a lot while they grow. After harvest, these nutrients are not often replaced naturally through the roots. To keep soil healthy and help gardens grow, we need to add these elements back with fertilizers.
Breaking Down Soil NPK
Just like carbohydrates, fats, and proteins give energy to the human body, certain nutrients are important for plants. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are essential for plant nutrition. Making sure your plants get the right balance of these important nutrients helps them grow well and keeps your garden lively.
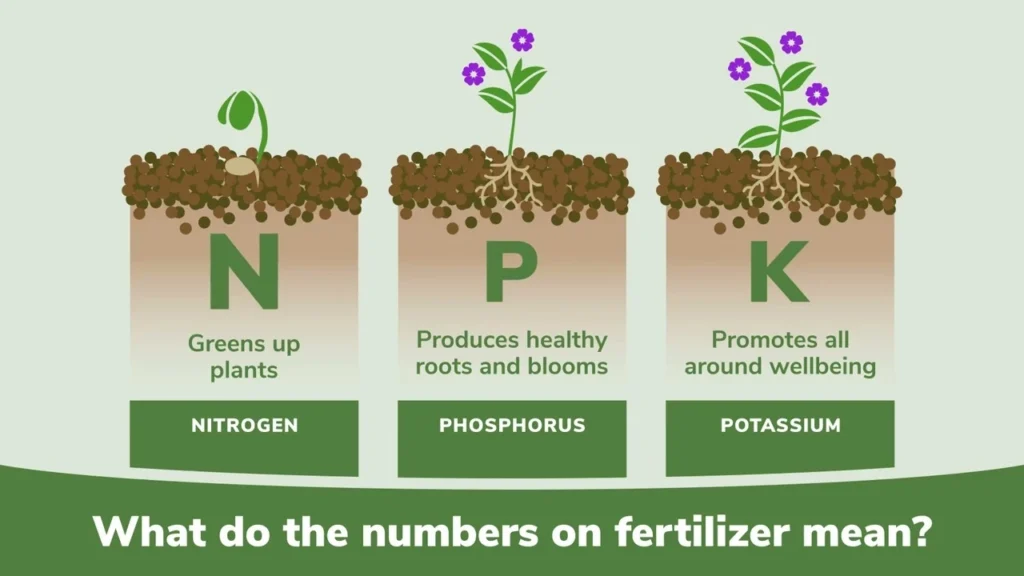
Nitrogen (N):
Nitrogen is represented by the letter “N” in NPK. It makes up a large part of the atmosphere, but plants cannot use it directly. Organic matter needs to be added to the soil. This helps make nitrogen available for plants to absorb.
This nutrient is essential for making chlorophyll and photosynthesis. It is important for the growth of green leaves. A lack of nitrogen can slow down plant growth. It can cause stunted stems, smaller yellow leaves, and early leaf drop. For green plants and vegetable crops, adding nitrogen regularly is very important.
However, using too much nitrogen can be risky. It can lead to oversized cells and weak leaves. These weak leaves are more likely to get diseases. It can also cause issues with how plants use carbohydrates. This can harm their health. It’s always important to maintain moderation.
Phosphorus (P):
In NPK ratios, “P” means phosphorus. This nutrient is important for helping plants adapt to tough conditions and survive cold periods. During growth phases, this nutrient builds up in sprouts and root tips.
This helps with ongoing development. In reproductive stages, it moves to seeds or fruits. When a plant does not have enough phosphorus, older leaves show signs of this. Symptoms include slow growth, less branching, purplish-red stems, or early fruit drop.
Natural sources of phosphorus are seabird droppings, fish bones, and shells from seafood. These can be dried, ground into powder, and applied near plant roots.
Phosphorus supplementation is very important for larger flowers and fruits. However, too much phosphorus can age plants too quickly. It can also make it hard for plants to absorb other nutrients like zinc, iron, and manganese. This can hurt their growth.
Potassium (K):
Potassium is shown as “K” in NPK. Plants take in potassium as the K+ ion. It helps plants balance other nutrients. It also controls the flow of water and air in their tissues.
Potassium is important for chemical reactions in plants. It helps them make and store starches, sugars, oils, and proteins. It also helps them resist drought and diseases better. Using potassium fertilizer in the late growth stages helps make fruit bigger, better in quality, and more colorful.
Plants with potassium deficiency often show clear signs. These signs include yellowing leaf tips and edges. They also have less resistance to drought and cold. Such plants are more likely to get diseases.
Additionally, their stems may become weak, making them easier to fall or break. To fight potassium deficiency, plants need enough potassium. You can add natural potash fertilizers to help.
One common option is ashes from burned plant material. This nutrient-rich fertilizer can be used in two ways. You can apply it directly to the base of plants. You can mix it with water to create a liquid for spraying on leaves. It is important to use potassium carefully.
Too much potassium can block the absorption of calcium and other nutrients. This can increase the risk of rot and disease, which can harm crop yield.
The Importance of Measuring Soil NPK
Monitoring soil nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) is important. It helps us check and manage nutrient levels in the soil. Regular soil tests show what nutrients are in the soil. This helps us fertilize plants based on their specific needs.
This process helps fix nutrient problems. It ensures a balanced supply of nutrients. This promotes higher crop yields and improves the health and beauty of garden plants.
Methods to Test Soil NPK
All soils have different amounts of NPK elements that are important for plant growth. External factors like weather and geography often cause changes in soil health.
Gardeners and farmers need to spot nutrient deficiencies quickly. This helps keep the soil in good condition. Luckily, tools like soil NPK detectors make soil management easier by giving accurate information.
1. **Soil NPK Tester**
This portable device measures the levels of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in the soil directly. Gardeners can easily use the probe. They can insert it into the soil and get instant data. The tool is compact and practical. It is great for keeping soil healthy in gardens using science.
2. **Soil NPK Sensor**
This strong sensor is made for large farms or estates. It has a high durability with an IP68 rating. This means it can resist tough conditions, is waterproof, and won’t corrode.
You can install several sensors in different field locations. The data collected at each point is sent through 485 signals to a cloud platform for central monitoring. Users can access real-time information from their smartphones or computers. This helps them add nutrients on time.
3. **Handheld Soil Analyzer**
This handy tool is a great choice for people who want to skip complicated wiring or real-time monitoring. It displays results obtained from soil sensors measuring NPK levels. It also supports connections with other sensors for temperature, humidity, and pH levels. This makes it a complete solution for managing different soil elements.
4. **7-in-1 Soil Sensor**
For farms that need a lot of monitoring, this advanced sensor measures several things at once. It checks nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, temperature, moisture, pH values, and electrical conductivity with its five probes. This device is cost-effective and multifunctional. It provides a complete solution for keeping soil healthy in real time.