sensors in agriculture List And Benefits
What advantages do modern agriculture sensors offer?
A sensor can find data and turn it into an electrical signal or useful information. It follows rules to help with tasks like sending, processing, storing, showing, recording, and controlling information. As IoT sensor technology grows, sensors are used more in fields like farming and industry.
In smart farming, farmers use sensors. These sensors measure many things. They check air temperature, humidity, and soil moisture. They also check the soil’s pH, how bright the light is, and the levels of carbon dioxide.
The sensors in agriculture gather real time data at various stages of crop growth. This includes planting, growing, and harvesting.
Farmers use sensors to check water and fertilizer levels. These sensors measure conductivity and pH levels. The control system also keeps track of the mixed fertilizer.
What precisely are sensors used?
Agricultural sensors are made up of plant information sensors and environmental sensors. We make plant information sensors to track how plants grow. These sensors measure how plants grow and check their growing conditions.
Environmental sensors are used to watch and study the environment where plants grow. This includes water, soil, and air. They help us see changes in the environment. This also makes it better for plant health to grow.
What constitutes a smart agriculture real time monitoring system?
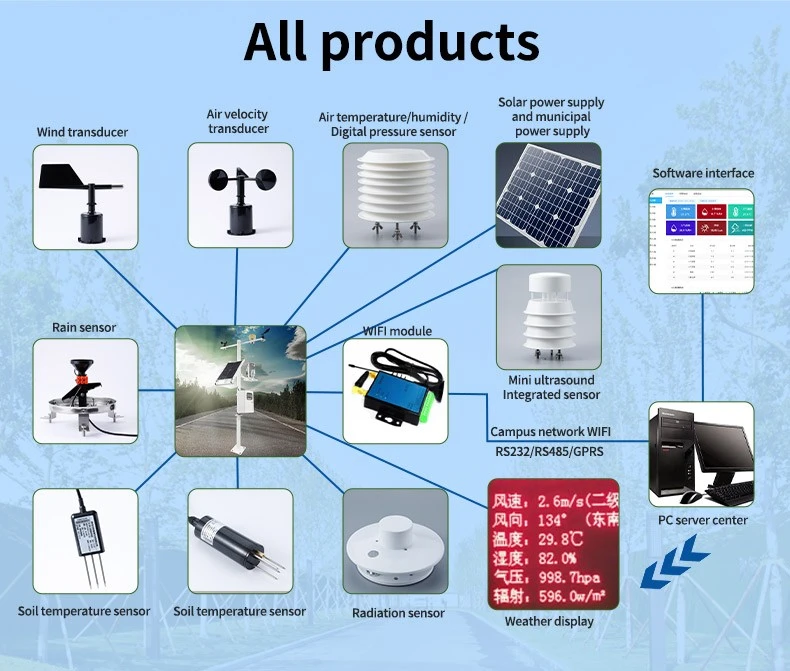
Catalog of agricultural sensors
Sensors are very important. With IoT technology, we can gather data on plants and animals. This lets us watch their changes in real time.
In farming, types of sensors are very important. They help with tasks like fertilizing, spraying pesticides, and watering crops. Sensors track soil conditions, pests, humidity, and other plant data.
This information helps us find the best times for fertilizing, spraying, and watering. It also helps us save resources and protect the environment better than old farming methods.
1.Air temperature and humidity sensor
The sensor measures air temperature and humidity in farming areas. It can track temperatures from -40℃ to +80℃. The humidity can range from 0% to 100%.
It has a wall-mounted design, which makes it easy to install in greenhouses or shaded areas with good air flow. When used outside, it can be placed in a solar radiation shield next to a weather station to gather weather data.
The coda sensor uses a temperature and humidity measurement unit from Switzerland. It also has a strong microprocessor chip from the US. This setup ensures accurate measurements and reliable communication.
2. Soil moisture sensor
The soil moisture sensor is an important tool in farming. It helps find out how much water crops need. Too much or too little moisture can hurt plant growth.
When soil moisture is just right, it helps roots take in water. It also helps leaves release water. This balance is important for healthy crop growth.
The coda soil moisture sensor measure the moisture by checking the soil’s dielectric constant. This method meets international standards for testing. It can accurately show the moisture content in various types of soil.
3. Soil pH Sensor
Keeping the right soil pH is important for strong plant growth. The coda soil pH sensor works by touching the soil directly with its electrochemical sensors.
It uses current from a chemical reaction. This current affects the pH data. The host device reads this data and shows it as numbers.
We make the sensor’s steel needle from a special alloy. This alloy resists corrosion from acids and alkalis. We seal the casing with black flame-retardant epoxy resin. This gives it an IP68 protection level.
4. Light Sensor
The light sensor has three main parts: a transmitter, a receiver, and a detection circuit. Each part is made of electronic elements. It does not need time for mechanical operations, so it can measure light intensity quickly. This sensor can measure light intensity from 0 to 200,000 Lux and responds fast.
In greenhouse farming, light sensors are very helpful. They help farmers know how much sunlight plants receive. These sensors measure the light saturation point and the light compensation point. Both are important for plant growth.
Farmers can use this information to change the lighting conditions. This helps them grow crops better and increase yields.
5. CO2 sensor
Crops take in CO₂ from the air for photosynthesis. This process helps them create nutrients needed for growth. Studies show that higher carbon dioxide levels can boost plant photosynthesis.
The Coda carbon dioxide sensor uses advanced infrared technology to detect and measure CO₂ levels in the air. It responds quickly and accurately, solving issues with short lifespan and drift found in older sensors. Its standard measurement range is from 0 to 5000 ppm. It also has a feature that helps with temperature changes.
6. Atmospheric Pressure Sensor
An air pressure sensor can sense changes in atmospheric pressure. Farmers can use this sensor to track weather changes, like drops in pressure and shifts in wind speed. This helps them prevent disasters and reduce crop damage.
The sentence is in active voice. It shows how farmers (the subject) take action to harvest (the verb) mature crops based on predictions.
7.precipitation Gauge
A precipitation gauge is a tool used to measure rainfall. Rain and snow help restore moisture in the soil. The outdoor tipping bucket gauge gives accurate readings with few errors. When used with an evaporation sensor, it helps analyze soil moisture better.
This device is important for farming sensors. It tracks rainfall levels and when it occurs. This information helps improve watering methods.
What benefits do agricultural sensors provide?
Irrigation system management:
By checking monitor soil moisture, humidity, and weather data collection, we can measure soil moisture levels well. This helps make sure the soil gets enough water when it needs it. We can use the coda multi-layer soil sensor in irrigation systems for automatic watering. We can control the irrigation schedule and amount using mobile apps.
Set up a system to watch for pests and diseases. Place insect traps around the farm. Use pesticide sprayers when needed to keep optimizing crop healthy.
Sensors can track temperature, humidity, air pressure, and more in real-time. This helps control pests and diseases better in the fields.
A system that tracks insects and has a weather sensor helps farmers choose the best insecticide.
Optimize fertilizer management:
We can learn more about soil health conditions. We do this by checking the levels of dissolved oxygen, metal ions, and hydrogen ions in the soil.
This helps us see what crops need and improve how we use fertilizer. A water-fertilizer machine can help farmers to make informed decisions. It checks soil nutrients and adds fertilizers on its own. This makes fertilizer use better and cuts down on waste.
Boost planting efficiency:
Sensors are important for studying weather data. They help manage and care for crops as they grow. For example, sensors that measure light and temperature are useful in various weather and climate conditions. They help us understand and manage the environment for growing crop conditions. This can make production more efficient.
Promote sustainable growth:
Agricultural sensors help farmers check how land is used. They can reduce wastewater and emissions. This reduces harm to the environment and helps with sustainable development efforts.
We mainly use sensors in farming to monitor things. This is especially true for water and fertilizer systems. These sensors check the conductivity, pH, and temperature of the fertilizer solution. Then, the data appears on an LCD screen.
It is also sent to the water and fertilizer management system for more processing.
The sensors that measure soil conductivity and pH have memory chips. They can store data for two days for conductivity and three days for pH. These sensors use accurate analog-to-digital conversion and micro-processing technology. They can gather data and adjust for temperature on their own.
Traditional precision agriculture relies a lot on manual labor and simple tools. It has shown many weaknesses compared to modern farming.
Today’s farming uses the Internet of Things and sensors. This technology gives us accurate and timely information about crop growth. It helps make better planting plans. It reduces labor and improves crop types. It also increases quality and yield.